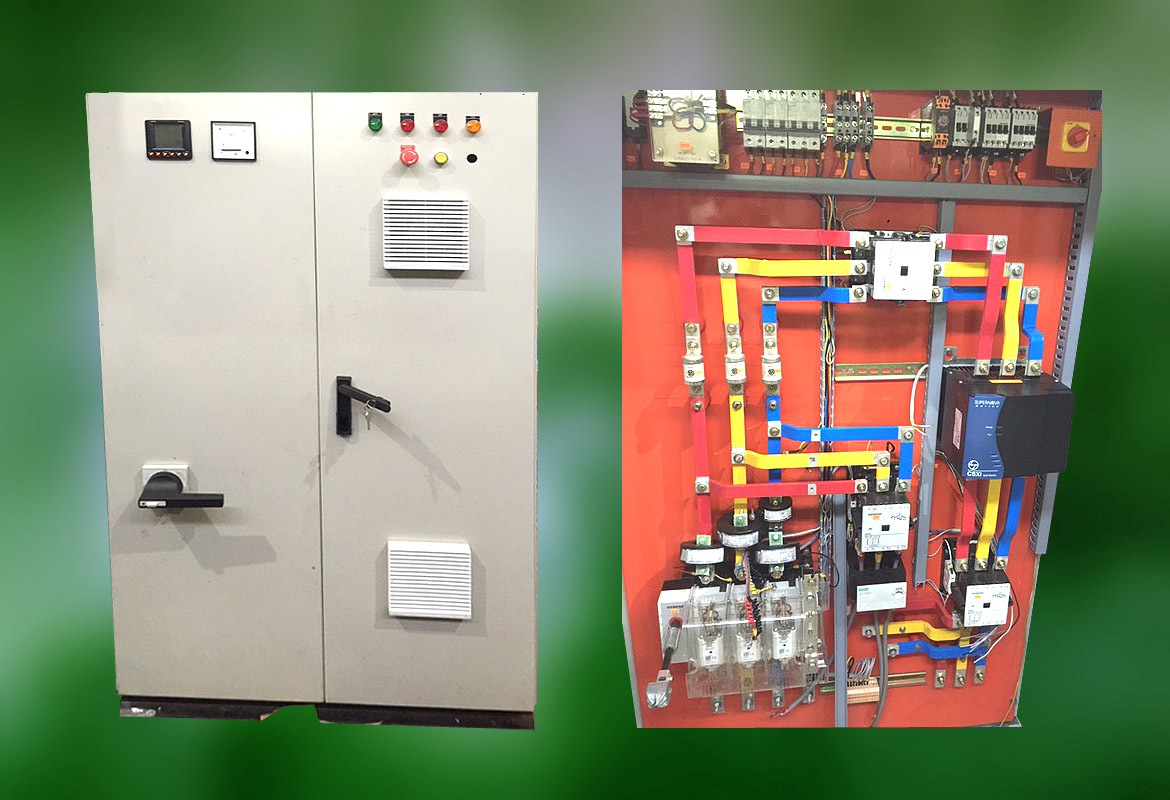
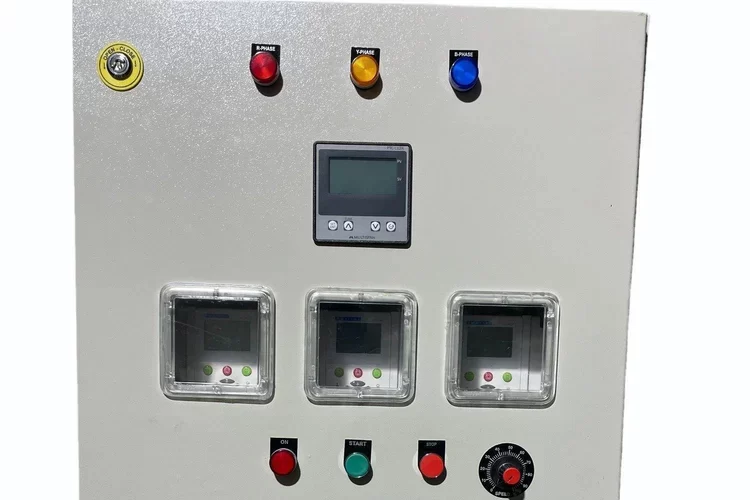
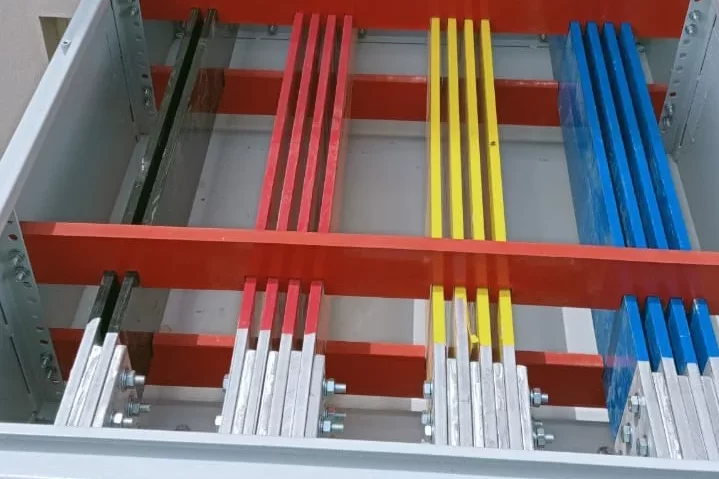
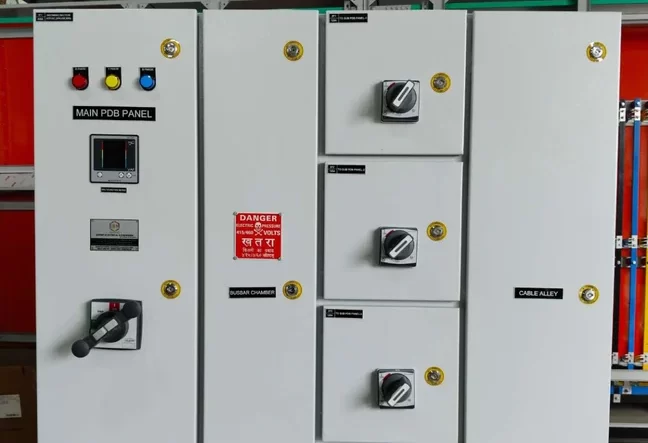
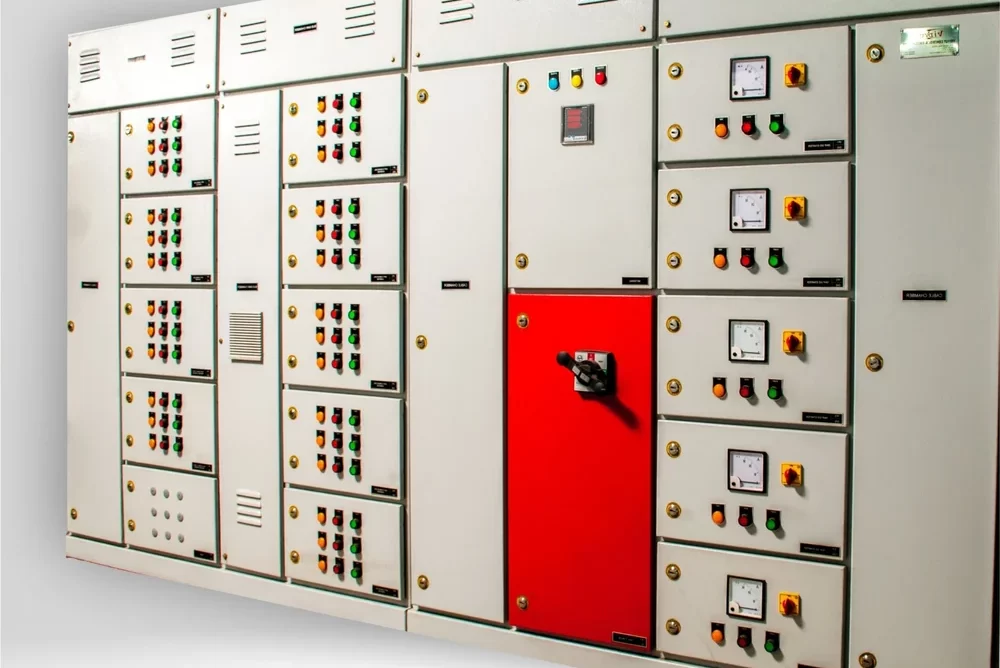
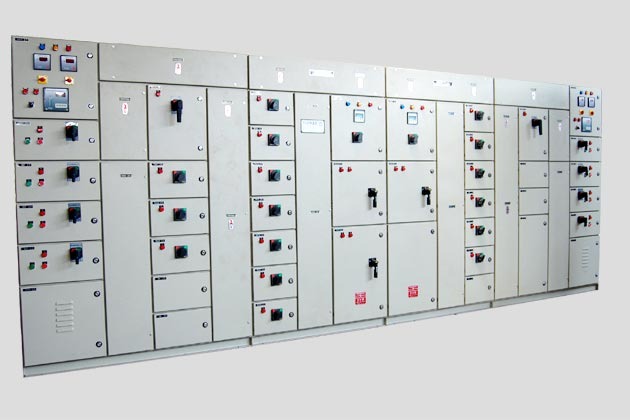
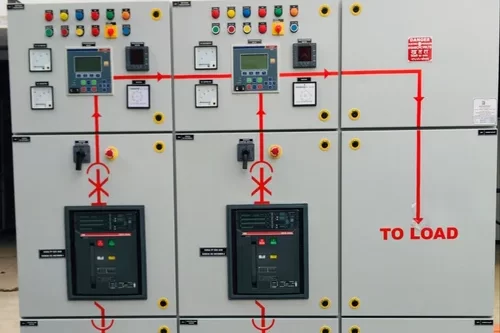
VFD and SOFT Starter Panel
A VFD and Soft Starter Panel is a specialized electrical panel designed to control and manage electric motors using Variable Frequency Drives (VFDs) and soft starters. These devices are employed to enhance motor control, optimize performance, and protect equipment in various industrial and commercial applications. Here’s a detailed explanation of each component and the purpose of the panel:
Key Features of a VFD and SOFT Starter Panel:
- Integrated Control:Provides centralized control and monitoring for both VFDs and soft starters, simplifying operation and maintenance.
- Customization: Can be customized to include additional features such as remote monitoring, communication interfaces, and protective relays.
- Safety and Protection: Includes protective devices and features to safeguard the motor and panel components.
- Energy Efficiency: Optimizes motor operation to achieve energy savings and reduce operational costs.
- User Interface: May include Human-Machine Interface (HMI) panels or digital displays for ease of use and monitoring.
In a VFD and Soft Starter Panel, various electrical abbreviations and symbols are used to represent the components, functions, and control elements involved. Here’s a comprehensive list of common abbreviations and symbols you might find in such panels:
VFD – Variable Frequency Drive
Function: Controls motor speed and torque by varying the frequency and voltage of the power supply.
SS – Soft Starter
Function: Gradually increases and decreases the voltage to the motor to reduce mechanical and electrical stress during start-up and shut-down.
HMI – Human-Machine Interface
Function: Provides a user interface for interacting with the VFD and soft starter, including configuration and monitoring.
PLC – Programmable Logic Controller
Function: Manages and automates the operation of the VFD and soft starter based on programmed logic.
CT – Current Transformer
Function: Measures the current flowing through the circuit and provides a scaled-down signal for monitoring and control.
PT – Potential Transformer
Function: Measures the voltage in the circuit and provides a scaled-down signal for monitoring and control.
RTD – Resistance Temperature Detector
Function: Measures the temperature of the motor or surrounding environment.
OLR – Overload Relay
Function: Protects the motor from overheating by detecting overload conditions.
MCB – Miniature Circuit Breaker
Function: Provides overcurrent protection for low-power circuits within the panel.
MCCB – Molded Case Circuit Breaker
Function: Protects electrical circuits from overloads and short circuits.
RCD – Residual Current Device
Function: Detects earth faults and disconnects the circuit to prevent electric shock.
EMC – Electromagnetic Compatibility
Function: Refers to the ability of the VFD and soft starter to operate without causing or being affected by electromagnetic interference.
PWM – Pulse Width Modulation
Function: A technique used by VFDs to control the power delivered to the motor by varying the pulse width of the electrical signal.
RTU – Remote Terminal Unit
Function: Collects data from field devices and sends it to the central control system for monitoring and control.
SCADA – Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition
Function: A system for real-time monitoring and control of the VFD and soft starter through a centralized interface.
VFD Symbol:
Symbol: Typically represented by a rectangle with a variable frequency label or icon.
Function: Indicates the location of the Variable Frequency Drive in the panel.
Soft Starter Symbol:
Symbol: Often represented by a rectangle with a soft starter label or icon.
Function: Indicates the location of the soft starter in the panel.
Motor Symbol (M):
Symbol: A circle with the letter “M” inside or a rectangle with a motor icon.
Function: Represents the electric motor being controlled by the VFD or soft starter.
Contactor Symbol (K):
Symbol: A rectangle with the letter “K” inside, often with a set of contacts represented by lines.
Function: Represents a contactor used for switching the motor on and off.
Overload Relay Symbol (OLR):
Symbol: A rectangle with the letters “OLR” or an icon depicting a relay.
Function: Indicates the location of the overload relay for motor protection.
Circuit Breaker Symbol (CB):
Symbol: A rectangle with the letters “CB” or a standard circuit breaker icon.
Function: Represents a circuit breaker for overcurrent protection.
Current Transformer Symbol (CT):
Symbol: A circle with a line passing through it or a rectangle with the letters “CT.”
Function: Represents a current transformer used for monitoring current.
Potential Transformer Symbol (PT):
Symbol: A rectangle with the letters “PT” or an icon depicting a transformer.
Function: Represents a potential transformer used for measuring voltage.
Resistance Temperature Detector Symbol (RTD):
Symbol: A rectangle or circle with “RTD” or a thermometer icon.
Function: Indicates a device used for temperature measurement.
Human-Machine Interface Symbol (HMI):
Symbol: A screen or panel icon with the letters “HMI.”
Function: Represents the interface for user interaction with the VFD and soft starter.
Fuse Symbol (F):
Symbol: A rectangle or square with the letter “F” inside.
Function: Represents a fuse used for overcurrent protection.
Alarm Symbol (AL):
Symbol: A triangle with an exclamation mark or a bell icon.
Function: Indicates an alarm or warning condition.
Indicator Light Symbol ( ):
Symbol: A circle or square with a lightbulb icon.
Function: Represents an indicator light showing the status of the VFD or soft starter.
Emergency Stop Symbol (E-STOP):
Symbol: A red button icon with “E-STOP” or a similar marking.
Function: Represents an emergency stop button for immediate shutdown.
Timer Relay Symbol (TR):
Symbol: A rectangle with the letters “TR” or an icon depicting a clock.
Function: Indicates a timer relay used for time-based control.
A VFD and Soft Starter Panel is used to manage and control electric motors through the integration of Variable Frequency Drives (VFDs) and soft starters. This panel enhances motor performance, extends equipment life, and improves operational efficiency across various industrial and commercial applications. Here’s a detailed overview of the uses for a VFD and Soft Starter Panel:
1. Variable Speed Control:
VFD:
Function: Allows precise control over the speed of an electric motor by varying the frequency and voltage of the power supply.
Use: Adjusts motor speed to match the requirements of different processes, such as controlling the flow rate of pumps, the speed of conveyors, and the airflow in fans.
2. Smooth Start and Stop:
Soft Starter:
Function: Gradually increases and decreases the voltage supplied to the motor, reducing mechanical and electrical stress during start-up and shut-down.
Use: Reduces the impact on mechanical components and electrical systems, minimizing wear and tear and extending the lifespan of motors and equipment.
3. Energy Efficiency:
VFD:
Function: Optimizes energy consumption by adjusting motor speed to match load requirements.
Use: Reduces energy consumption and operating costs in applications with variable load conditions, such as HVAC systems, water pumps, and industrial processes.
4. Torque Control:
VFD:
Function: Regulates the torque delivered by the motor to ensure optimal performance.
Use: Provides smooth acceleration and deceleration, improves process control, and enhances the performance of equipment such as crushers and mixers.
5. Current Limiting:
Soft Starter:
Function: Limits the inrush current during motor start-up to protect the motor and reduce stress on the electrical supply network.
Use: Prevents electrical and mechanical damage by controlling the start-up current, particularly in high-power applications.
6. Motor Protection:
VFD and Soft Starter:
Function: Provides protection features such as overload protection, over-voltage, under-voltage, and short-circuit protection.
Use: Safeguards the motor and associated equipment from electrical faults and abnormal operating conditions.
7. Improved Process Control:
VFD:
Function: Allows for precise control over motor-driven processes, enhancing the overall quality and efficiency of operations.
Use: Optimizes the performance of processes such as mixing, heating, and material handling.
8. Reduced Mechanical Stress:
Soft Starter:
Function: Minimizes mechanical stress on the motor and associated components during start-up and stop.
Use: Extends the lifespan of mechanical parts, such as gears, bearings, and belts, by reducing sudden mechanical shocks.
9. Remote Monitoring and Control:
VFD and Soft Starter:
Function: Allows for remote monitoring and control of the motor and panel through communication interfaces.
Use: Enables operators to manage and monitor motor performance and panel status from a remote location, enhancing operational flexibility.
10. Integration with Automation Systems:
VFD and Soft Starter:
Function: Integrates with PLCs, SCADA systems, and other automation technologies for coordinated control.
Use: Facilitates the automation of complex processes and systems, providing centralized control and monitoring capabilities.
11. Reduced Maintenance Costs:
VFD and Soft Starter:
Function: Enhances reliability and reduces wear and tear on motors and mechanical components.
Use: Lowers maintenance costs and minimizes downtime by reducing the frequency of repairs and replacements.
12. Customizable Settings:
VFD:
Function: Provides customizable control settings to suit various applications and requirements.
Use: Allows for tailoring motor control strategies to specific processes, such as varying speed profiles for different production stages.
13. Improved Safety:
VFD and Soft Starter:
Function: Includes safety features such as emergency stop functions and fault alarms.
Use: Ensures safe operation of the motor and panel, protecting personnel and equipment from potential hazards.
14. Enhanced System Performance:
VFD and Soft Starter:
Function: Optimizes motor performance and efficiency.
Use: Improves the overall performance of systems such as water treatment facilities, manufacturing lines, and HVAC systems.
15. Flexibility in Applications:
VFD and Soft Starter:
Function: Provides flexibility in motor control for a wide range of applications.
Use: Suitable for various industries including water and wastewater management, manufacturing, mining, and HVAC.