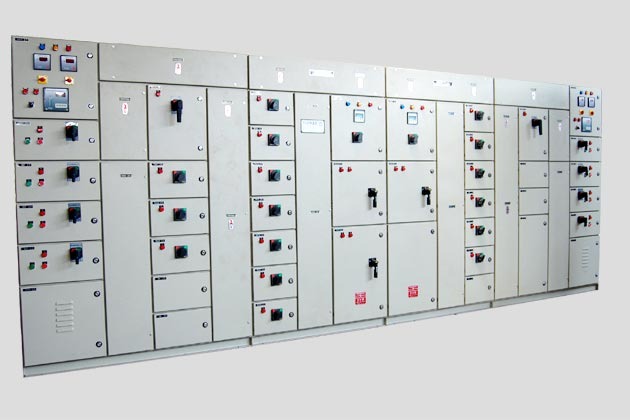
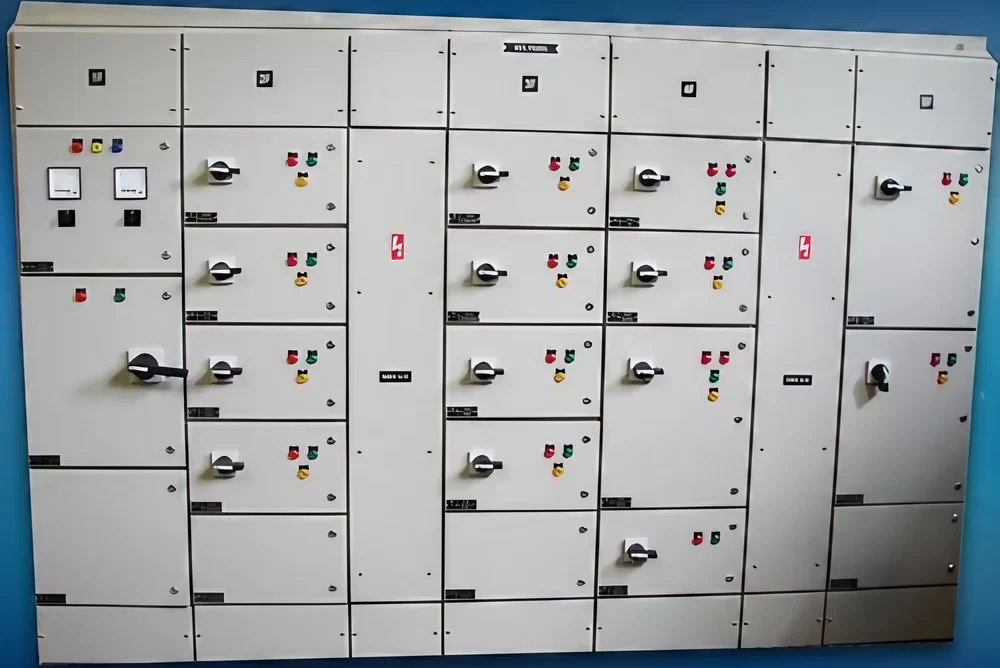
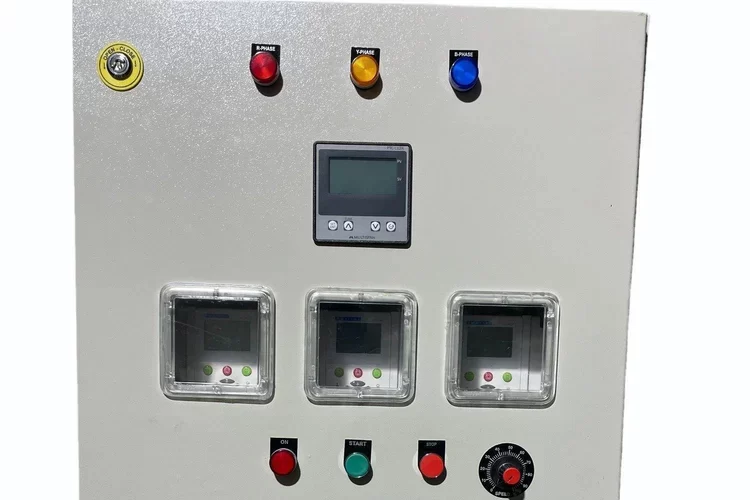
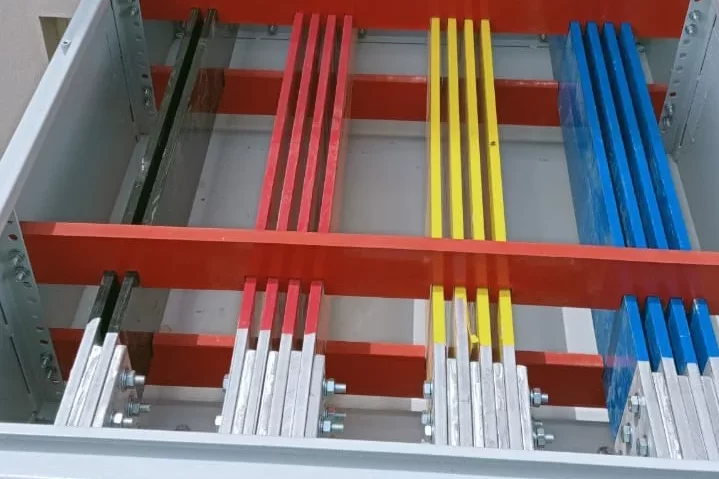
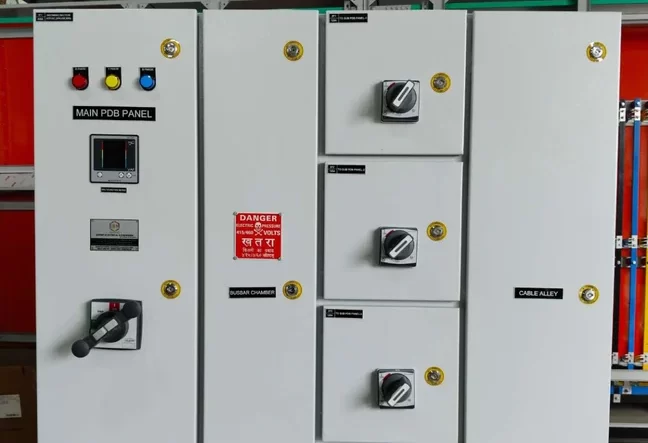
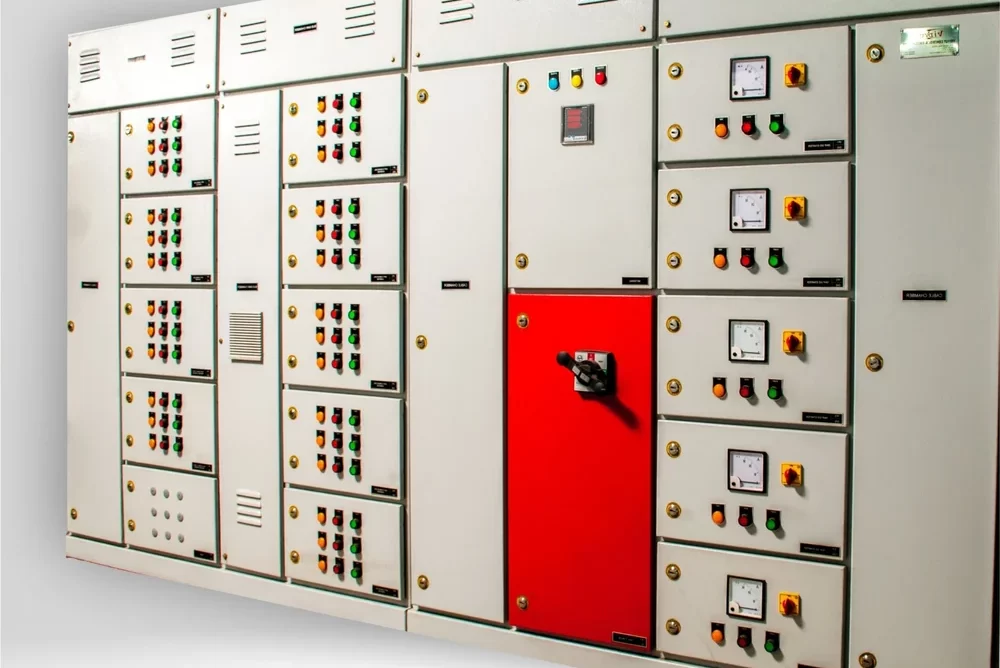
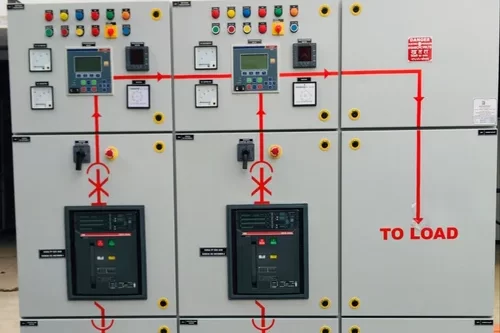
PCC Panel
A PCC (Power Control Center) panel is an essential component in industrial electrical systems, designed to manage the distribution and control of electrical power throughout a facility. It acts as a centralized unit where electrical power from the main power source is distributed to various sub-panels, machines, and equipment within an industrial or commercial setup.
Key Functions of a PCC Panel:
- Power Distribution: The PCC panel receives power from the main source and distributes it to different electrical loads, such as machinery, lighting, and other equipment. It ensures that the right amount of power is delivered to each section of the facility.
- Protection: The panel incorporates protective devices like circuit breakers, fuses, and relays to safeguard the electrical circuits from overloads, short circuits, and other faults. This helps prevent damage to equipment and ensures the safety of the facility.
- Monitoring: PCC panels are equipped with meters and indicators that allow operators to monitor various electrical parameters, such as voltage, current, power factor, and frequency. This monitoring capability is crucial for maintaining stable and efficient operations.
- Control: Operators can control the operation of different electrical circuits through the PCC panel. This includes starting and stopping motors, switching power to different parts of the facility, and adjusting settings to optimize performance.
- Isolation: The PCC panel can isolate certain sections of the electrical system for maintenance or in case of an emergency, allowing work to be done safely without shutting down the entire system.
- Automation Integration: Modern PCC panels can be integrated with automation systems, enabling remote monitoring and control, enhancing efficiency, and reducing the need for manual intervention.
In a Power Control Center (PCC) panel, various electrical abbreviations and symbols are used to represent different components, functions, and parameters. Understanding these abbreviations and symbols is crucial for reading electrical drawings and operating the panel effectively.
Circuit Breaker Symbol – A rectangular symbol with a line passing through it, representing a circuit breaker.
Transformer Symbol – Two parallel lines with zigzag lines between them, representing a transformer.
Motor Symbol – A circle with an “M” inside, representing an electric motor.
Fuse Symbol – A small rectangle with a line across it, representing a fuse.
Earth/Ground Symbol – A line with three descending horizontal lines, representing the earth or ground connection.
Contactor Symbol – A rectangle with lines representing the coil and contacts.
Relay Symbol – Similar to a contactor symbol, but often with additional indicators for the contacts.
Push Button Symbol – A circle with a line through it, representing a push-button switch.
Lamp Symbol – A circle with a small cross inside, representing an indicator lamp.
Resistor Symbol – A zigzag line, representing a resistor.
Capacitor Symbol – Two parallel lines, sometimes with a gap, representing a capacitor.
NO and NC Contacts Symbol – An open or closed switch symbol, representing normally open (NO) or normally closed (NC) contacts.
Rectifier Symbol – A diode symbol with a line and triangle, representing rectification.
Current Transformer (CT) Symbol – A circle with the letter “CT” inside, representing a current transformer.
Potential Transformer (PT) Symbol – A circle with the letter “PT” inside, representing a potential transformer.
Grounding Symbol – Three horizontal lines of different lengths stacked vertically.
AC – Alternating Current
DC – Direct Current
V – Voltage
A – Ampere (Current)
Hz – Hertz (Frequency)
kW – Kilowatt (Power)
kVA – Kilovolt-Ampere (Apparent Power)
PF – Power Factor
MCB – Miniature Circuit Breaker
MCCB – Molded Case Circuit Breaker
ELCB – Earth Leakage Circuit Breaker
RCCB – Residual Current Circuit Breaker
VFD – Variable Frequency Drive
CT – Current Transformer
PT – Potential Transformer
NO – Normally Open (Contacts)
NC – Normally Closed (Contacts)
SPDT – Single Pole Double Throw (Switch)
DPST – Double Pole Single Throw (Switch)
OLR – Overload Relay
RTD – Resistance Temperature Detector
ATS – Automatic Transfer Switch
TP – Triple Pole (Switch or Breaker)
TNS – Three-phase Four-wire with Separate Neutral and Earth
KWH – Kilowatt Hour (Energy Consumption)
CB – Circuit Breaker
DOL – Direct On Line (Starter)
ATS – Automatic Transfer Switch
1. Manufacturing Plants
Machinery Control: PCC panels are crucial in controlling and distributing power to various machinery and equipment. This ensures that each machine operates with the necessary power supply, facilitating smooth production processes.
Process Automation: In automated production lines, PCC panels are integrated with control systems to manage the power requirements of different sections, improving efficiency and reducing downtime.
2. Power Generation and Distribution
Power Plants: PCC panels manage the distribution of electricity generated in power plants to the grid or to other facilities, ensuring stable and efficient power distribution.
Substations: They play a key role in distributing electricity from high-voltage transmission lines to lower-voltage distribution networks, which supply power to residential and commercial areas.
3. Commercial Buildings
Office Complexes: PCC panels control power distribution to various systems such as lighting, HVAC, elevators, and other critical infrastructure within large office buildings.
Shopping Malls: These panels manage power distribution to different stores, lighting systems, escalators, and air conditioning units, ensuring uninterrupted service.
4. Oil and Gas Industry
Refineries: PCC panels control the distribution of power to different processes within an oil refinery, such as distillation and cracking, ensuring safe and efficient operations.
Offshore Platforms: In offshore oil and gas exploration, PCC panels distribute power to drilling equipment, communication systems, and other critical operations on the platform.
5. Chemical and Petrochemical Plants
Process Control: PCC panels manage the power distribution to various process equipment like pumps, compressors, and reactors, which are vital for chemical processing.
Safety Systems: They are also integrated with safety systems to provide power to emergency shutdown systems, fire suppression systems, and other safety-critical infrastructure.
6. Mining Industry
Heavy Equipment Operation: PCC panels distribute power to heavy machinery such as conveyors, crushers, and drills, which are essential for mining operations.
Ventilation and Lighting: They ensure that power is consistently supplied to ventilation systems, lighting, and other critical support systems in underground and surface mining operations.
7. Water Treatment Plants
Pumping Stations: PCC panels control the power distribution to various pumps used in water treatment processes, including those for water intake, filtration, and distribution.
Monitoring Systems: They manage the power supply to monitoring and control systems that ensure the water treatment processes operate efficiently and within required parameters.
8. Hospitals and Healthcare Facilities
Critical Equipment Power Supply: PCC panels ensure that critical equipment such as life-support systems, imaging devices, and emergency lighting receive a stable power supply.
Backup Power Integration: They facilitate the integration of backup power systems like generators, ensuring that there is no interruption in power supply during emergencies.
9. Data Centers
Server Power Management: PCC panels manage the distribution of power to servers, cooling systems, and other essential infrastructure within data centers, ensuring continuous operation.
Redundant Power Systems: They are used to implement redundant power systems, providing backup power and ensuring high availability of data services.
10. Transportation Systems
Railway Stations: PCC panels control and distribute power to various systems in railway stations, including lighting, signaling, and communication systems.
Airports: They manage power distribution to essential airport systems such as runway lighting, baggage handling systems, and terminal operations.
These applications highlight the versatility and importance of PCC panels in ensuring reliable and efficient power distribution across a wide range of industries.