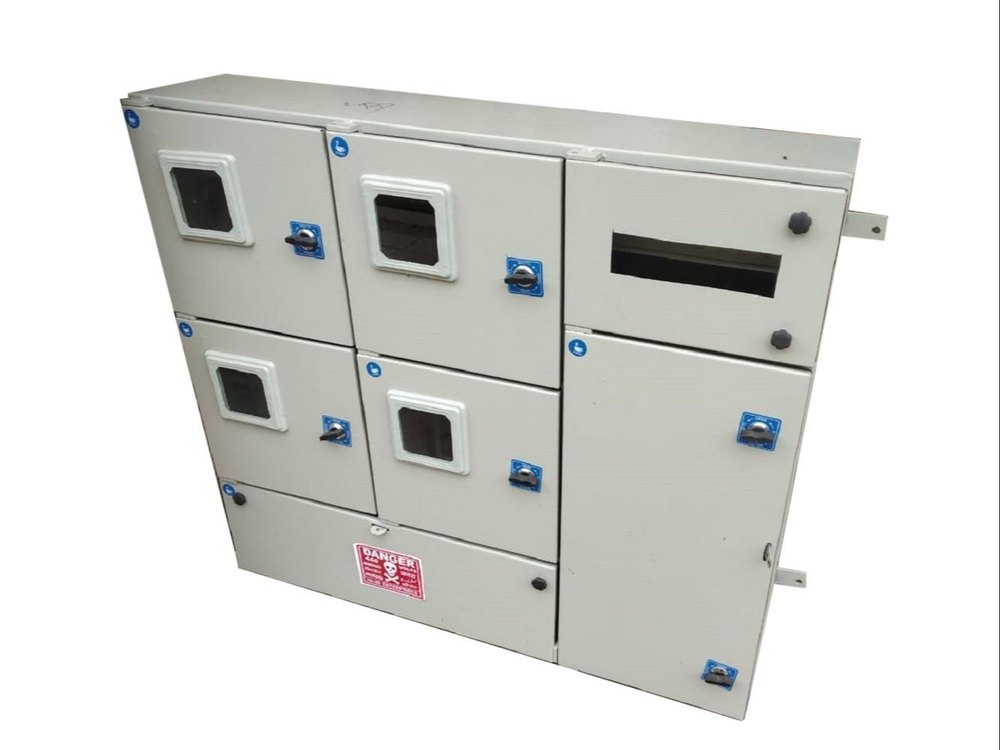
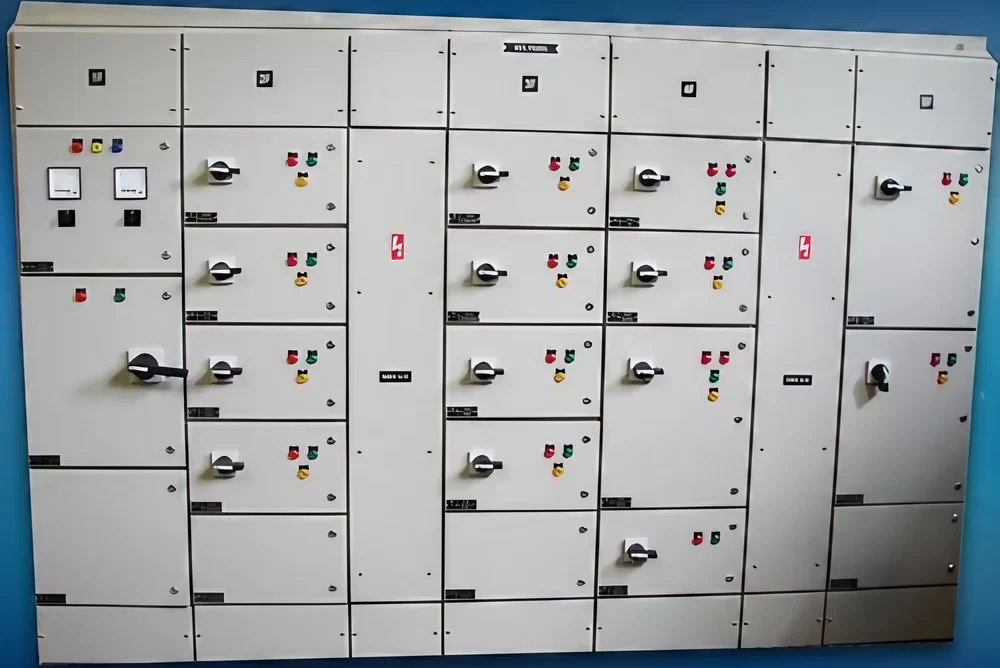
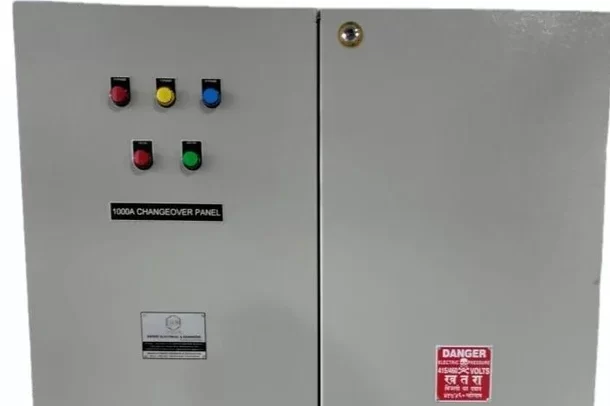
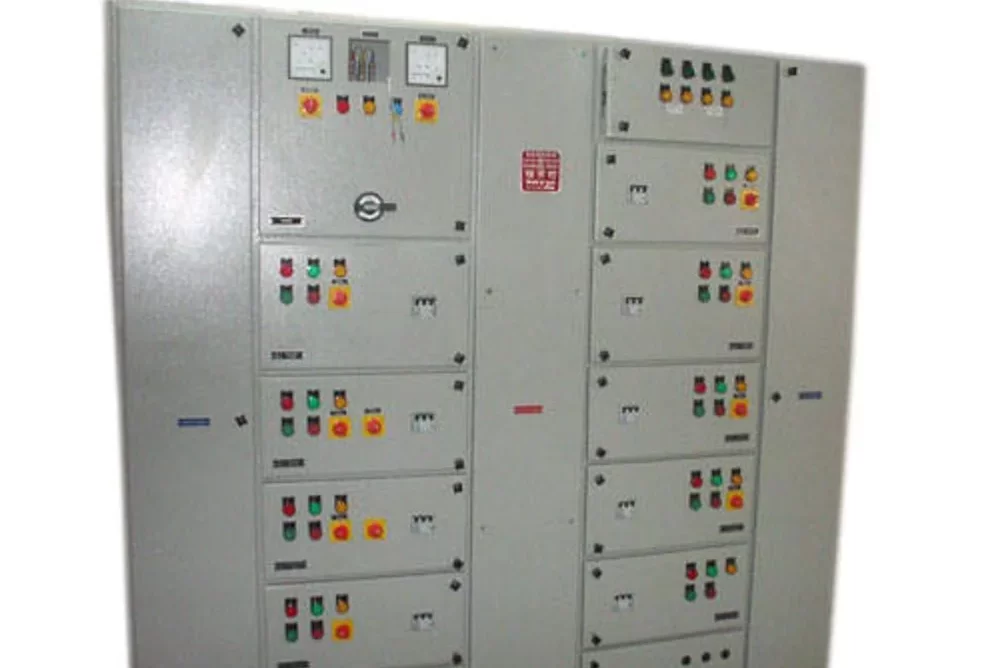
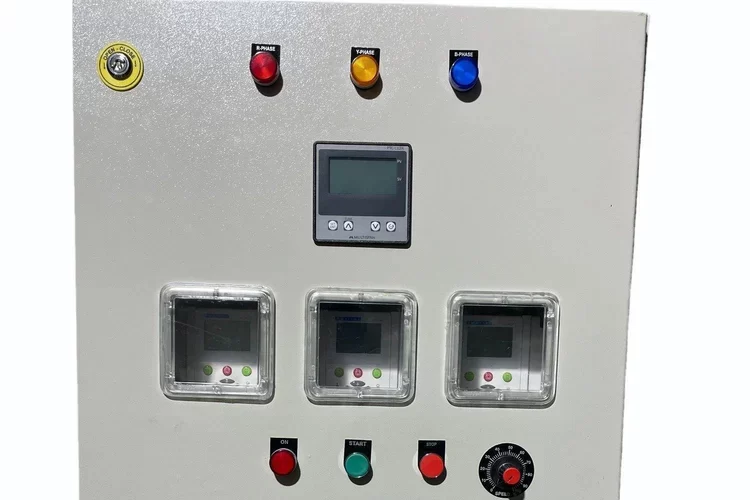
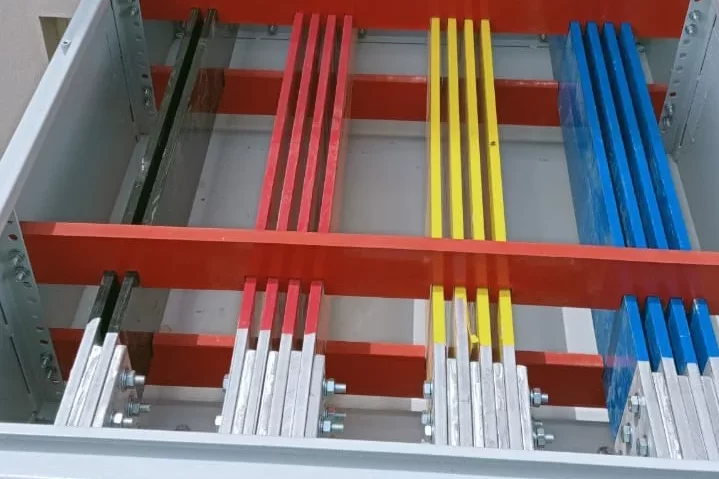
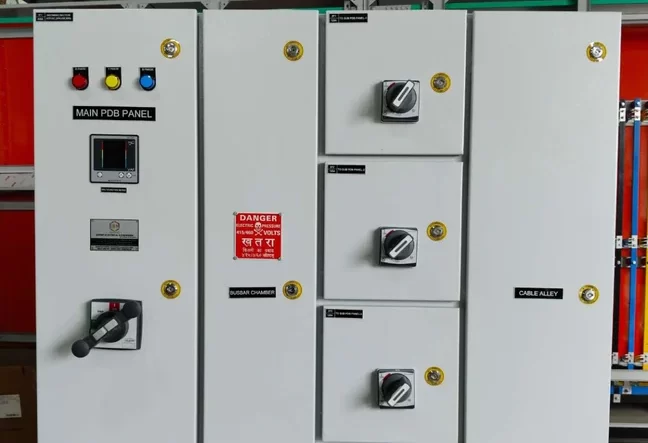
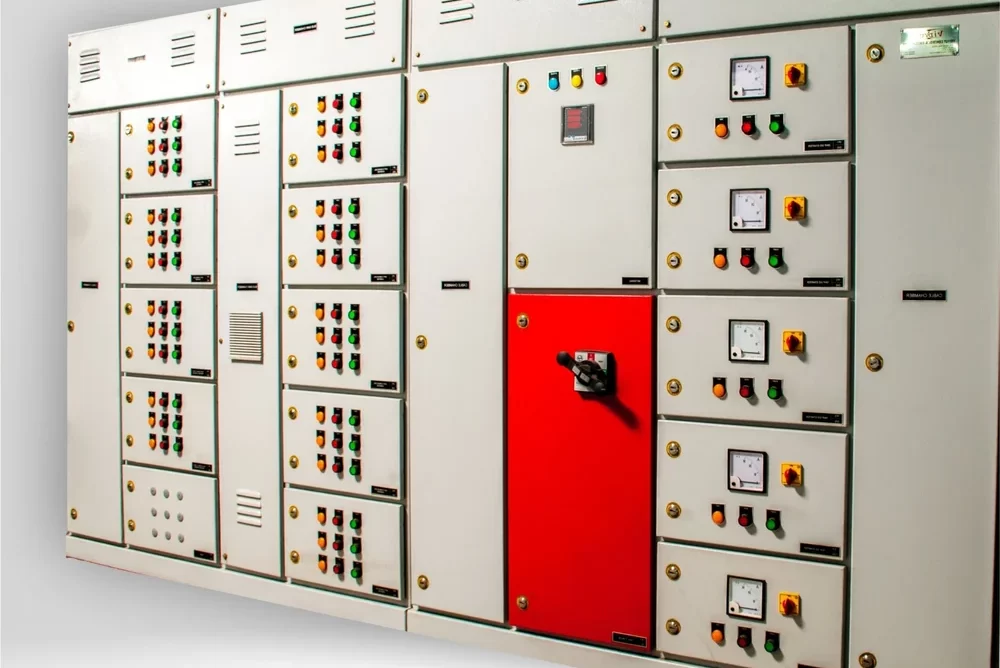
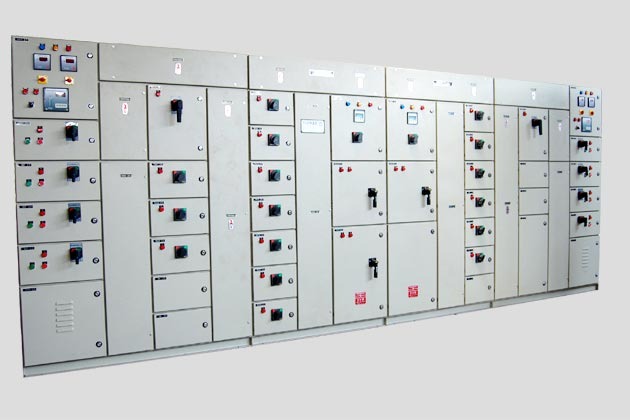
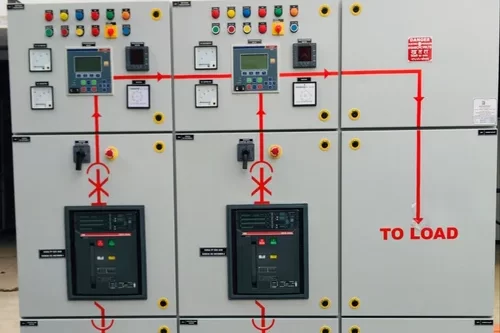
Meter Panel Board
A Meter Panel Board (or Metering Panel Board) is an electrical distribution panel used to house and manage electrical meters for monitoring and measuring electrical consumption. It is an essential component in power distribution systems, providing a centralized location for metering equipment and related control devices.
Key Features of a Meter Panel Board:
- Metering Equipment:Houses various types of electrical meters, such as energy meters, voltage meters, and current meters, used to measure electrical parameters.
- Control and Protection Devices: Includes control devices like switches and breakers, as well as protective devices like fuses or circuit breakers to ensure safe operation.
- Display and Monitoring: Provides a means to view and monitor electrical readings and performance metrics.
- Wiring and Connections: Facilitates the connection of electrical circuits to the meters and other components. It ensures proper routing and organization of wiring.
- Enclosure: Protects the metering equipment and wiring from environmental factors and unauthorized access.
- Auxiliary Components: May include additional components such as control relays, communication interfaces, and data logging devices.
In a Meter Panel Board, various electrical abbreviations and symbols are used to represent the components, connections, and functions within the system. Here’s a guide to some common abbreviations and symbols you might encounter in a meter panel board:
MPB – Meter Panel Board
EM – Energy Meter
VM – Voltage Meter
AM – Ampere Meter (Current Meter)
CB – Circuit Breaker
MCCB – Molded Case Circuit Breaker
RCB – Residual Current Breaker
RCD – Residual Current Device
RCCB – Residual Current Circuit Breaker
SPD – Surge Protection Device
CT – Current Transformer
PT – Potential Transformer
MCB – Miniature Circuit Breaker
F – Fuse
ISOL – Isolator
SW – Switch
PDB – Power Distribution Board
L1, L2, L3 – Live Conductors (Phases)
N – Neutral
GND – Ground (Earth)
V – Voltage
A – Ampere (Current)
KW – Kilowatt (Power)
kWh – Kilowatt-hour (Energy)
CT Ratio – Current Transformer Ratio
MFM – Multifunction Meter
VFD – Variable Frequency Drive (if integrated for metering)
RTU – Remote Terminal Unit (for communication)
Energy Meter Symbol: A rectangle or square with labels indicating energy metering (e.g., kWh meter). It may also include a small dial or digital display symbol.
Voltage Meter Symbol: A circle with a “V” inside or a rectangle with a digital display symbol.
Ampere Meter Symbol:A circle with an “A” inside or a rectangle with a digital display symbol.
Circuit Breaker Symbol: A rectangle with a switch icon or a line with a break, indicating the circuit can be opened or closed.
Fuse Symbol: A rectangle or small circle with a line through it.
Isolator Symbol:A switch icon, often with an open circle or a diagonal line.
Surge Protection Device (SPD) Symbol: A rectangle with a zigzag line or a lightning bolt symbol.
Current Transformer (CT) Symbol:A small rectangle or square with coils or loops, representing the current sensing device.
Potential Transformer (PT) Symbol: Similar to the CT symbol but often labeled “PT” or with a lower case “v.”
Ground Symbol: A vertical line with three descending horizontal lines.
Neutral Symbol: A straight horizontal line or a line with an “N” label.
Live Wire Symbols (L1, L2, L3): Lines labeled L1, L2, L3, often used to denote the three phases of AC power.
Multifunction Meter Symbol: A rectangle with multiple display options or a digital screen representation.
Remote Terminal Unit (RTU) Symbol: A rectangle or square with communication lines, indicating remote data transmission.
Power Distribution Board (PDB) Symbol: A larger rectangle or square indicating the distribution point with internal lines for connections.
Switch Symbol: A simple break or a switch icon in a line, showing where the circuit can be manually opened or closed.
A Meter Panel Board is used primarily for measuring and monitoring electrical power consumption and other related parameters in various types of electrical distribution systems. Here are some key uses and applications of a Meter Panel Board:
1.Measurement of Electrical Consumption:
Purpose: The primary function of a Meter Panel Board is to measure the amount of electrical energy consumed by a building, facility, or specific area. This is done using energy meters (kWh meters) that record the usage over time.
Example: In an apartment building, a meter panel board records the electricity consumption of each apartment, allowing for accurate billing.
2.Monitoring Electrical Parameters:
Purpose: Besides energy consumption, meter panel boards often monitor other electrical parameters such as voltage, current, power factor, and frequency. This helps in ensuring the stability and efficiency of the electrical system.
Example: In an industrial plant, the meter panel board monitors the voltage and current to ensure machines operate within safe limits.
3.Energy Management:
Purpose: Meter panel boards play a critical role in energy management systems by providing real-time data on energy usage. This data can be used to optimize energy consumption, reduce waste, and lower costs.
Example: A commercial building uses a meter panel board to track energy use patterns and implement energy-saving strategies.
4.Billing and Revenue Generation:
Purpose: Accurate metering is essential for billing purposes, especially in multi-tenant buildings, commercial complexes, and industrial facilities. Each tenant or department can be billed based on their actual energy consumption.
Example: In a shopping mall, each store is billed for its specific electricity usage as recorded by the meter panel board.
5.Load Management:
Purpose: By monitoring the load on different circuits, a meter panel board helps in managing the distribution of power and avoiding overloads or underutilization of electrical systems.
Example: An industrial facility uses a meter panel board to distribute loads evenly across different circuits, preventing any one circuit from being overloaded.
6.Compliance and Regulatory Requirements:
Purpose: Meter panel boards are often required by law or regulation to ensure accurate metering and reporting of electrical consumption. This is particularly important for utilities and large facilities.
Example: Utility companies use meter panel boards to comply with regulations that require accurate measurement of electricity provided to customers.
7.Fault Detection and Maintenance:
Purpose: By continuously monitoring electrical parameters, meter panel boards can help in detecting faults such as voltage sags, surges, or power quality issues. This allows for timely maintenance and repairs.
Example: A meter panel board in a data center alerts maintenance staff to a sudden drop in voltage, preventing potential damage to sensitive equipment.
8.Sub-Metering:
Purpose: In large facilities, meter panel boards can be used for sub-metering, which involves measuring the consumption of individual departments, areas, or pieces of equipment. This is useful for cost allocation and management.
Example: A university campus uses a meter panel board to track energy usage in different buildings and allocate costs accordingly.
9.Data Collection for Analysis:
Purpose: Meter panel boards collect and store data on energy usage, which can be analyzed to identify trends, inefficiencies, and opportunities for improvement.
Example: A manufacturing plant analyzes data from the meter panel board to identify machines that are consuming excessive energy, leading to process improvements.
10.Integration with Building Management Systems (BMS):
Purpose: Meter panel boards can be integrated with BMS to provide a centralized platform for monitoring and controlling all aspects of a building’s energy use.
Example: A smart building uses a meter panel board connected to its BMS to automatically adjust lighting and HVAC systems based on occupancy and time of day.