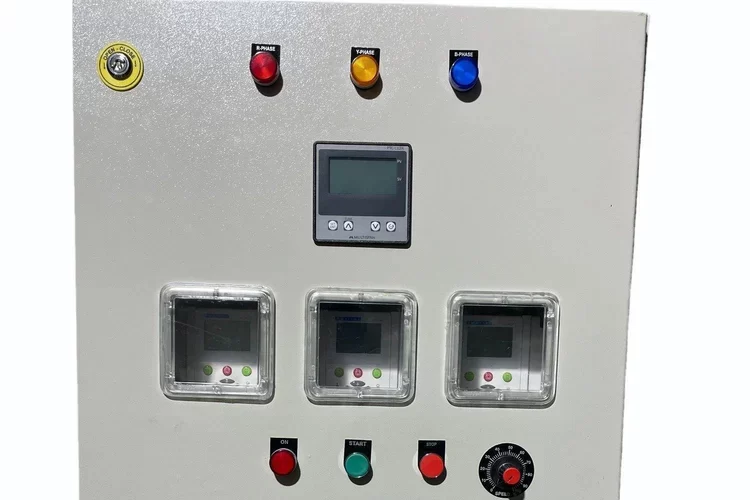
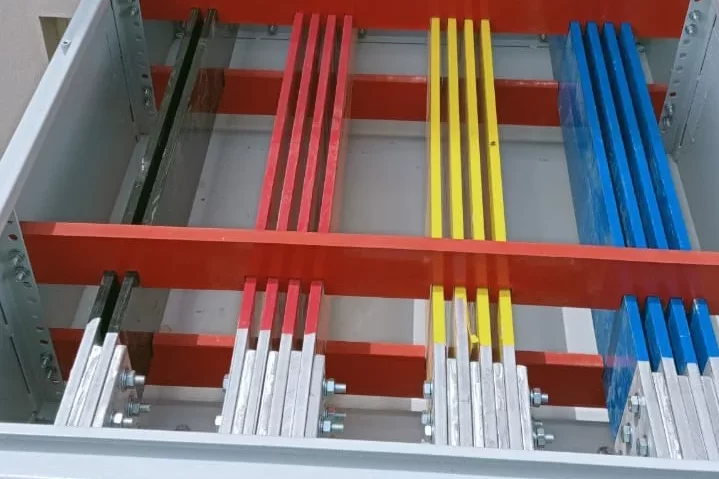
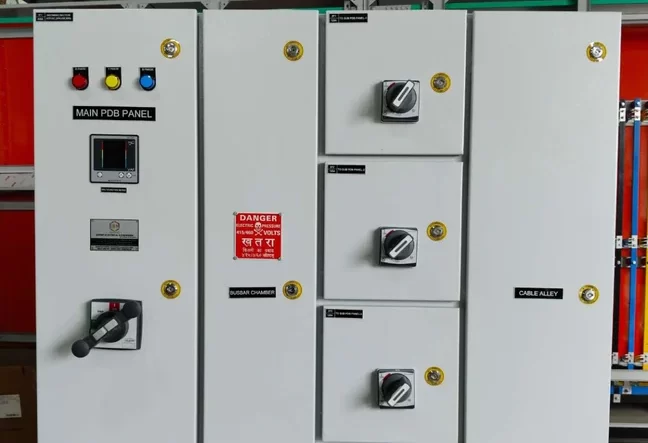
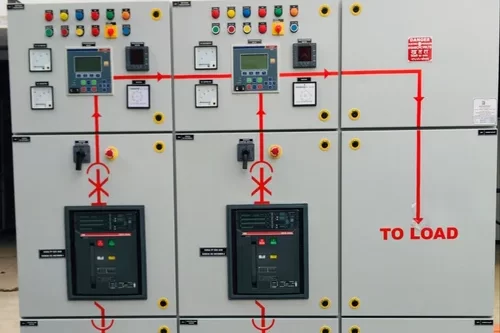
Intelligent Motor Control Center
An Intelligent Motor Control Center (IMCC) is an advanced type of Motor Control Center (MCC) that integrates smart technologies, communication capabilities, and advanced control functions to provide enhanced management, monitoring, and protection of motor systems in industrial and commercial applications. Unlike traditional MCCs, which primarily focus on starting and stopping motors, an IMCC offers real-time data collection, diagnostics, predictive maintenance, and remote control, improving operational efficiency, safety, and reliability.
Key Features of Intelligent Motor Control Centers:
1.Advanced Communication:
Function: IMCCs are equipped with communication interfaces (such as Ethernet, Modbus, Profibus) that allow for seamless integration with plant-wide automation systems and SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition) systems.
Benefit: Enables real-time monitoring and control of motor operations from a centralized location, improving responsiveness and decision-making.
2.Real-time Monitoring:
Function: Continuously monitors motor performance, including parameters like voltage, current, temperature, and operating hours.
Benefit: Provides valuable insights into motor health, energy consumption, and operational efficiency, enabling proactive maintenance and energy management.
3.Predictive Maintenance:
Function: Uses data analytics and condition monitoring to predict potential motor failures before they occur.
Benefit: Reduces unplanned downtime, extends motor life, and minimizes maintenance costs by scheduling maintenance activities only when necessary.
4.Enhanced Motor Protection:
Function: Offers advanced protection features, such as overload protection, phase failure detection, ground fault detection, and thermal protection.
Benefit: Protects motors from damage due to electrical faults, ensuring safe and reliable operation.
5.Energy Management:
Function: Monitors and optimizes energy usage, helping to identify inefficiencies and reduce energy costs.
Benefit: Supports sustainability initiatives and helps achieve energy efficiency targets by optimizing motor operations.
6.Remote Control and Diagnostics:
Function: Allows operators to remotely start, stop, and control motors, as well as perform diagnostics and troubleshooting.
Benefit: Increases operational flexibility and reduces the need for on-site personnel, especially in hazardous or hard-to-reach areas.
7.Data Logging and Reporting:
Function: Logs operational data, faults, and maintenance activities, and generates reports for analysis and compliance purposes.
Benefit: Provides a comprehensive record of motor performance and maintenance history, aiding in audits, compliance, and continuous improvement efforts.
8.Scalability and Flexibility:
Function: IMCCs can be easily expanded or reconfigured to accommodate additional motors or changes in the control system architecture.
Benefit: Offers long-term adaptability to meet evolving operational needs without significant downtime or costs.
8.Integration with Automation Systems:
Function: Seamlessly integrates with Distributed Control Systems (DCS), Programmable Logic Controllers (PLC), and other automation systems for coordinated process control.
Benefit: Enhances overall process automation, improving efficiency and reducing human error.
9.User-friendly Interface:
Function: Often includes Human-Machine Interface (HMI) panels for easy operation, monitoring, and control.
Benefit: Simplifies interaction with the control system, making it easier for operators to manage motor operations and troubleshoot issues.
In an Intelligent Motor Control Center (IMCC), electrical abbreviations and symbols are used to represent various components, functions, and control elements involved in motor management and monitoring. Here’s a list of common abbreviations and symbols you might find in IMCC schematics:
IMCC – Intelligent Motor Control Center
Refers to the advanced panel integrating smart technologies for motor control.
PLC – Programmable Logic Controller
Used for controlling and automating motor operations within the IMCC.
HMI – Human-Machine Interface
Provides a user interface for operators to interact with the IMCC.
VFD – Variable Frequency Drive
Controls the speed and torque of the motor by varying the frequency and voltage of the power supply.
CT – Current Transformer
Measures current flowing through a circuit and provides a reduced current for monitoring or control.
PT – Potential Transformer
Measures voltage in a circuit and provides a scaled-down voltage for protection, metering, or control.
RTD – Resistance Temperature Detector
Measures temperature by correlating the resistance of the RTD element with temperature.
MCCB – Molded Case Circuit Breaker
Protects electrical circuits from overloads and short circuits.
MCB – Miniature Circuit Breaker
Provides overcurrent protection for low-power circuits.
OLR – Overload Relay
Protects motors from overheating due to excessive current.
RCD – Residual Current Device
Detects earth faults and disconnects the circuit to prevent electric shock.
SCADA – Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition
A system for real-time monitoring and control of the IMCC.
DT – Digital Transformer
Refers to transformers with digital monitoring and control capabilities.
FSC – Fieldbus Segment Controller
Manages communication between field devices and the central control system over a fieldbus network.
RTU – Remote Terminal Unit
Collects data from field devices and sends it to the central control system.
DCS – Distributed Control System
A control system that manages multiple process control functions across a distributed network.
PWM – Pulse Width Modulation
A technique used to control the power delivered to the motor by varying the width of the pulses.
ED – Emergency Disconnect
A switch or device for manually disconnecting power in case of an emergency.
Motor Symbol (M)
Represents an electric motor within the IMCC.
Circuit Breaker Symbol (CB)
Indicates a circuit breaker used for protection against overcurrent or short circuits.
Variable Frequency Drive Symbol (VFD)
Represents a VFD used to control the speed of the motor.
Overload Relay Symbol (OLR)
Symbol for an overload relay used to protect the motor from overheating.
Current Transformer Symbol (CT)
Represents a current transformer used for monitoring current levels.
Potential Transformer Symbol (PT)
Represents a potential transformer used for voltage measurement.
RTD Symbol (RTD)
Indicates a resistance temperature detector used for temperature measurement.
Residual Current Device Symbol (RCD)
Represents an RCD for earth fault protection.
HMI Symbol (HMI)
Represents the Human-Machine Interface panel for user interaction.
PLC Symbol (PLC)
Indicates a programmable logic controller used for automation and control.
SCADA Symbol (SCADA)
Represents the SCADA system for real-time monitoring and control.
Remote Terminal Unit Symbol (RTU)
Represents an RTU used for remote data collection and control.
Fieldbus Segment Controller Symbol (FSC)
Indicates the controller for managing fieldbus communications.
Emergency Disconnect Symbol (ED)
Represents an emergency disconnect switch for manual power disconnection.
Contactor Symbol (K)
Indicates a contactor used for switching the motor on and off.
Fuse Symbol (F)
Represents a fuse used for overcurrent protection.
Timer Relay Symbol (TR)
Indicates a timer relay used for controlling time-based operations.
Alarm Symbol (AL)
Represents an alarm indicator for fault conditions or system alerts.
Indicator Light Symbol ( )
Shows the status of the system or specific components.
Busbar Symbol ( )
Represents a busbar used for distributing electrical power within the IMCC.
An Intelligent Motor Control Center (IMCC) is used to enhance the management, control, and monitoring of electric motors in various industrial and commercial applications. The IMCC integrates advanced technologies and communication capabilities to provide real-time data, predictive maintenance, and efficient motor control. Here’s a detailed look at the uses of an IMCC:
1. Enhanced Motor Control:
Function: Provides precise control over motor operations, including starting, stopping, speed regulation, and torque adjustment.
Application: Used in manufacturing processes, conveyor systems, and other applications where accurate motor control is crucial for operational efficiency.
2. Real-Time Monitoring:
Function: Continuously tracks motor performance parameters such as current, voltage, temperature, and operational status.
Application: Enables operators to monitor the health of motors in real time, ensuring optimal performance and early detection of potential issues.
3. Predictive Maintenance:
Function: Analyzes data from motors to predict potential failures before they occur.
Application: Helps schedule maintenance activities proactively, reducing unexpected downtime and extending the life of motors and associated equipment.
4. Energy Management:
Function: Monitors and optimizes energy consumption of motors to reduce operating costs.
Application: Applied in facilities with high energy usage, such as large industrial plants, to identify and address inefficiencies and improve energy efficiency.
5. Advanced Protection:
Function: Provides comprehensive protection against overloads, short circuits, phase failures, and other electrical faults.
Application: Ensures the safety and reliability of motor operations in critical applications, such as HVAC systems and water treatment plants.
6. Remote Monitoring and Control:
Function: Allows for remote access and control of motor operations via communication networks and control systems.
Application: Useful for facilities with geographically dispersed equipment or where on-site access is challenging, such as remote industrial sites or large commercial buildings.
7. Integration with Automation Systems:
Function: Integrates with Distributed Control Systems (DCS), Programmable Logic Controllers (PLC), and other automation systems for coordinated process control.
Application: Enhances overall process automation and efficiency in complex industrial operations, such as chemical processing and large-scale manufacturing.
8. Data Logging and Reporting:
Function: Records operational data, fault events, and maintenance activities, and generates reports for analysis.
Application: Supports decision-making, compliance, and continuous improvement efforts by providing detailed records of motor performance and maintenance history.
9. Improved Safety:
Function: Includes safety features such as emergency disconnects, alarms, and protective relays to safeguard personnel and equipment.
Application: Ensures safe operation in hazardous environments and reduces the risk of accidents and equipment damage.
10. Scalability and Flexibility:
Function: Offers scalability and flexibility to accommodate changing operational needs and expansions.
Application: Suitable for facilities that anticipate growth or changes in their motor control requirements, allowing for easy upgrades and modifications.
11. Customizable Control Settings:
Function: Provides customizable control settings for different motor applications and operational requirements.
Application: Allows tailoring of control strategies to specific processes, such as variable speed drives for pumps or fans.
12.Improved Operational Efficiency:
Function: Optimizes motor performance and minimizes downtime through advanced control and monitoring features.
Application: Enhances productivity and efficiency in manufacturing plants, water treatment facilities, and other industrial settings.
14. Support for Complex Processes:
Function: Manages and controls motors involved in complex processes with multiple parameters and interactions.
Application: Used in industries such as chemical processing, where precise control of motor-driven pumps and mixers is essential.
14. Data-Driven Decision Making:
Function: Provides actionable insights based on data analytics and performance metrics.
Application: Supports informed decision-making regarding maintenance, upgrades, and operational adjustments.
15. Regulatory Compliance:
Function: Helps meet regulatory requirements by providing accurate data and documentation for audits and inspections.
Application: Ensures compliance with industry standards and regulations in sectors like energy, manufacturing, and healthcare.
16. Enhanced System Integration:
Function: Facilitates seamless integration with other system components and control systems.
Application: Supports coordination of motor control with other automation and process control systems, improving overall system performance.
17. Support for Various Motor Types:
Function: Accommodates different types of motors, including AC, DC, and specialized motors.
Application: Provides versatile control solutions for a wide range of motor applications in diverse industries.
18. Operational Flexibility:
Function: Allows for flexible operation modes and configurations based on specific application needs.
Application: Useful in dynamic environments where operational requirements frequently change, such as in batch processing or seasonal operations.