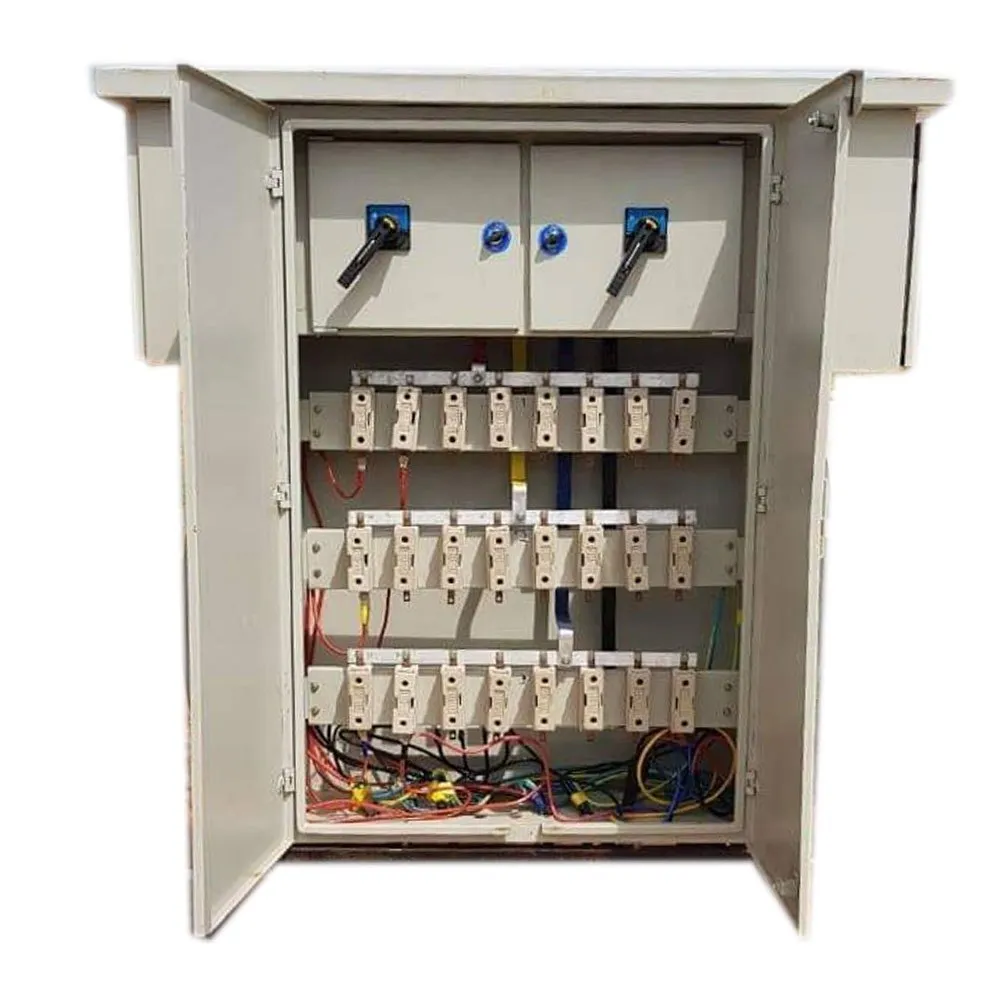
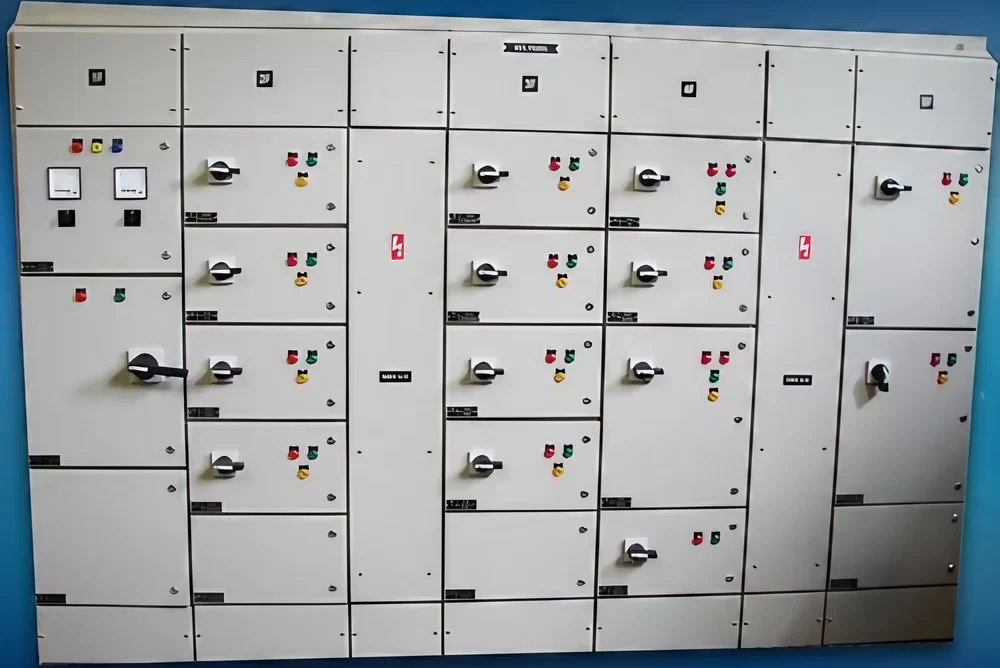
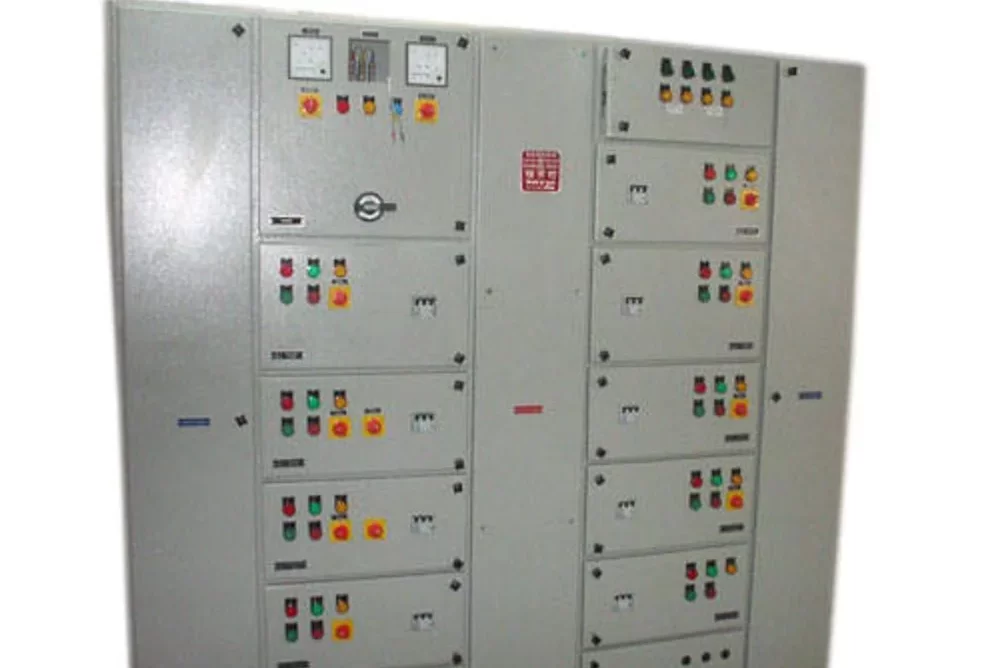
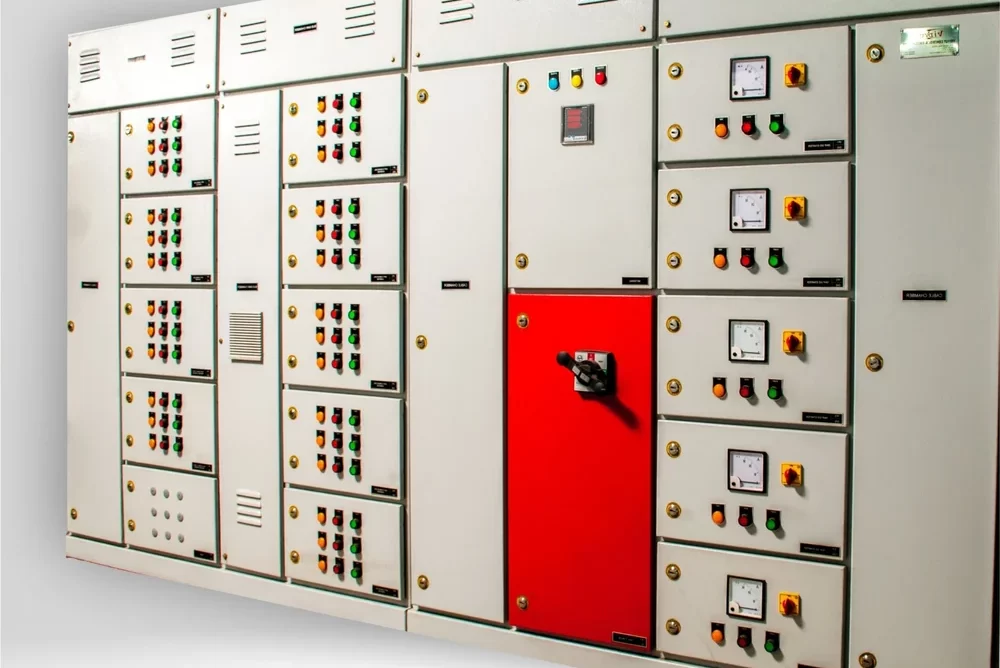
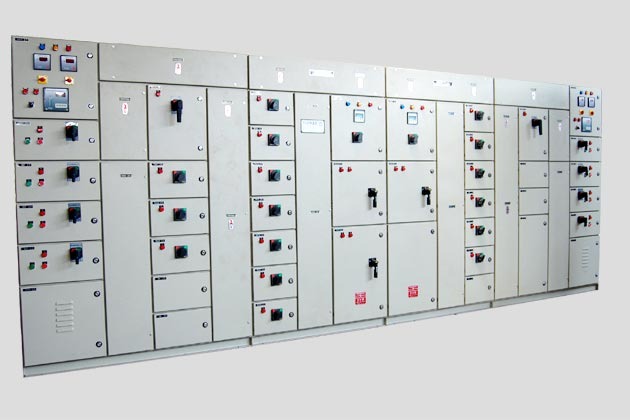
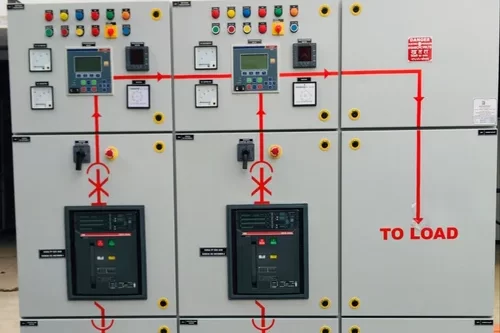
Feeder Pillar
A Feeder Pillar is an electrical distribution device used in electrical power systems to distribute electricity from a main source to various secondary circuits or feeders. It serves as an intermediary point between the main power supply and the end-users or different sections of a distribution network. Feeder pillars are commonly used in both urban and rural electrical distribution systems.
Key Functions of a Feeder Pillar:
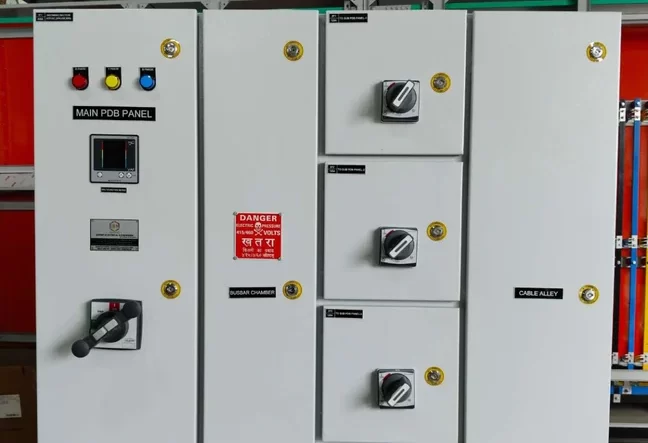
- Distribution Point: Feeder pillars act as a distribution point where electrical power is distributed to different feeders or circuits. They help in managing and controlling the distribution of electricity from a central point to various locations.
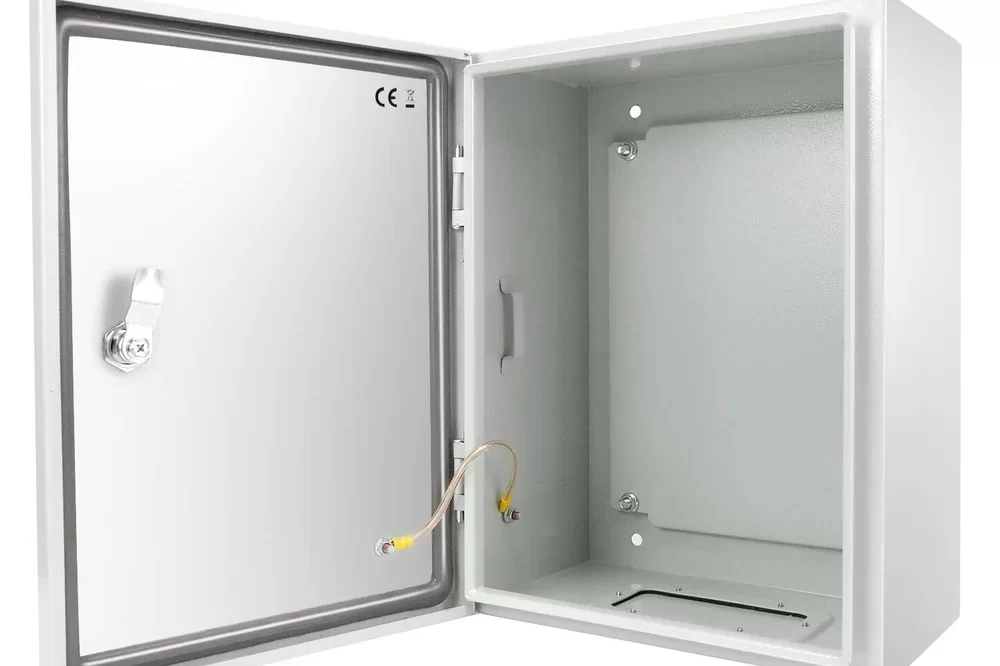
- Enclosure: They are housed in a weatherproof and robust enclosure, typically made of materials like metal or fiberglass, to protect the electrical components from environmental factors such as rain, dust, and temperature fluctuations.
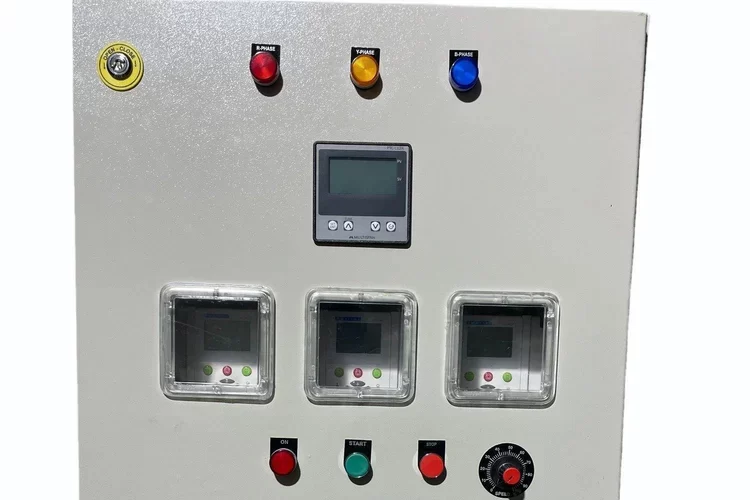
- Safety and Protection: Feeder pillars are equipped with various protection devices such as circuit breakers, fuses, and isolators to safeguard the electrical system from faults, overcurrents, and short circuits. They also often include metering equipment to monitor energy consumption.
- Access Points: They have access doors or panels that allow maintenance personnel to access the internal components for inspection, maintenance, and repairs. These access points are designed to ensure safety and ease of access.
-
Components:
Typical components found inside a feeder pillar include:
Circuit Breakers or Fuses: For protecting the circuits from overloads and short circuits.
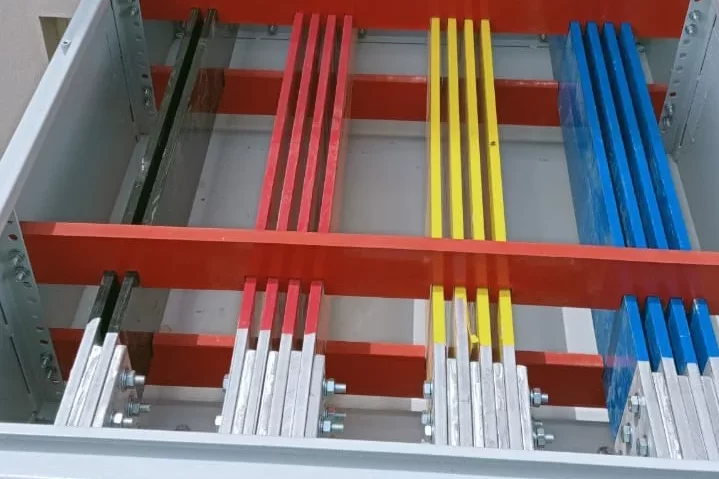
Busbars: For distributing electricity within the pillar.
Isolators: For disconnecting the circuits during maintenance.
Metering Equipment: For measuring energy consumption.
Control Equipment: For managing and monitoring the distribution of electricity. - Mounting:Feeder pillars can be installed above ground or partially buried, depending on the installation requirements and environmental conditions.
In feeder pillars, various electrical abbreviations and symbols are used to represent different components and functions. These are essential for understanding electrical diagrams, ensuring proper installation, operation, and maintenance. Here’s a guide to common abbreviations and symbols used in feeder pillars:
CB – Circuit Breaker
MCB – Miniature Circuit Breaker
MCCB – Molded Case Circuit Breaker
RCCB – Residual Current Circuit Breaker (Earth Leakage Circuit Breaker)
RCBO – Residual Current Circuit Breaker with Overcurrent Protection
ISOL – Isolator
CT – Current Transformer
PT – Potential Transformer (Voltage Transformer)
BU – Busbar
FUSE – Fuse
LT – Low Tension
HT – High Tension
E/M – Earth/Neutral
SPD – Surge Protection Device
M – Meter (Energy Meter)
NO – Normally Open (Contact)
NC – Normally Closed (Contact)
OLR – Overload Relay
AMP – Ampere (Current)
V – Voltage
W – Watt (Power)
kW – Kilowatt
kVAR – Kilovolt-Ampere Reactive (Reactive Power)
THD – Total Harmonic Distortion
Circuit Breaker Symbol:Represents a device that automatically interrupts the circuit in case of overload or short circuit.
Fuse Symbol:Represents a protective device that breaks the circuit when an overcurrent occurs.
Isolator Symbol:Represents a device used to disconnect a circuit for maintenance.
Current Transformer (CT) Symbol:Represents a device used to measure current and provide inputs to monitoring equipment.
Potential Transformer (PT) Symbol:Represents a device used to measure voltage and provide it to metering equipment.
Busbar Symbol:Represents a conductor that distributes electricity within the feeder pillar.
Meter Symbol:Represents an energy meter used to measure electrical consumption.
Surge Protection Device (SPD) Symbol:Represents a device that protects the system from voltage spikes.
Overload Relay Symbol:Represents a device that protects motors from overload conditions.
Earth/Earth Ground Symbol:Represents the grounding connection for safety.
Neutral Link Symbol:Represents the neutral connection point in the feeder pillar.
Terminal Block Symbol:Represents connection points for wiring within the pillar.
Control Switch Symbol:Represents manual switches or controls used for operating equipment.
Alarm or Indicator Light Symbol:Represents indicator lights used to show the status of the system.
Ventilation Fan Symbol:Represents a fan used to cool the interior of the feeder pillar.
HMI (Human Machine Interface) Symbol:Represents the interface used for monitoring and controlling the feeder pillar.
Feeder pillars are crucial components in electrical distribution systems, serving a range of functions depending on their application. Here’s a detailed look at where and why feeder pillars are used:
1.Urban Electrical Distribution:
Street Lighting: Feeder pillars are used to distribute power to street lighting systems, ensuring that streets and public spaces are well-lit and safe.
Commercial Areas: They distribute electricity to various commercial establishments, such as shops, offices, and malls, within urban environments.
2.Rural Electrical Distribution:
Agricultural Facilities: Feeder pillars are employed to provide electricity to irrigation systems, agricultural machinery, and farm buildings in rural areas.
Remote Villages: They help extend the reach of the electrical distribution network to isolated or less accessible rural locations.
3.Industrial Sites:
Manufacturing Plants: In industrial settings, feeder pillars distribute power to different sections of the plant, including machinery, equipment, and production lines.
Factories: They manage the distribution of electricity to various operational areas, improving efficiency and reliability.
4.Commercial Buildings:
Office Buildings: Feeder pillars are used to distribute power to different floors or sections of office buildings, managing the supply for lighting, HVAC systems, and office equipment.
Shopping Malls: They distribute electricity to various stores and common areas within shopping malls.
5.Public Infrastructure:
Traffic Signals: Feeder pillars provide power to traffic lights and signaling systems, ensuring smooth traffic flow and safety at intersections.
Public Facilities: They supply power to public facilities such as libraries, community centers, and sports complexes.
6.Utilities and Service Providers:
Power Distribution: Feeder pillars are integral to the power distribution network of utility companies, helping to manage and distribute electricity from substations to end-users.
Substation Integration: They act as a link between substations and local distribution networks, improving the efficiency of power delivery.
7.Renewable Energy Systems:
Wind and Solar Farms: Feeder pillars are used to distribute electricity generated from renewable sources to the grid or local consumers, ensuring effective integration of renewable energy.
Energy Storage Systems: They can also be used in conjunction with energy storage systems to manage the distribution of stored energy.
8.Transportation Systems:
Railways: Feeder pillars supply power to railway signaling systems, track switches, and other equipment necessary for railway operations.
Airports: They are used to distribute power to various airport facilities, including baggage handling systems, lighting, and terminals.
9.Healthcare Facilities:
Hospitals: Feeder pillars distribute power to different sections of hospitals, including critical care units, laboratories, and administrative areas, ensuring a reliable power supply.
Benefits of Using Feeder Pillars:
Efficient Distribution: They allow for the organized and efficient distribution of electrical power from a central source to various feeders and end-users.
Safety: Equipped with protective devices such as circuit breakers and fuses, feeder pillars enhance the safety of the electrical system by preventing faults and overloads.
Durability: The robust and weatherproof design ensures that feeder pillars withstand harsh environmental conditions and continue to function reliably.
Ease of Maintenance: Access doors and panels facilitate easy maintenance and repairs, ensuring that the electrical distribution system remains operational and efficient.
Flexibility: Feeder pillars can be configured to accommodate different types of electrical loads and distribution needs, making them versatile components in electrical systems.
Feeder pillars play a vital role in managing and distributing electrical power across various applications, ensuring efficient and reliable power supply to different sectors and locations.