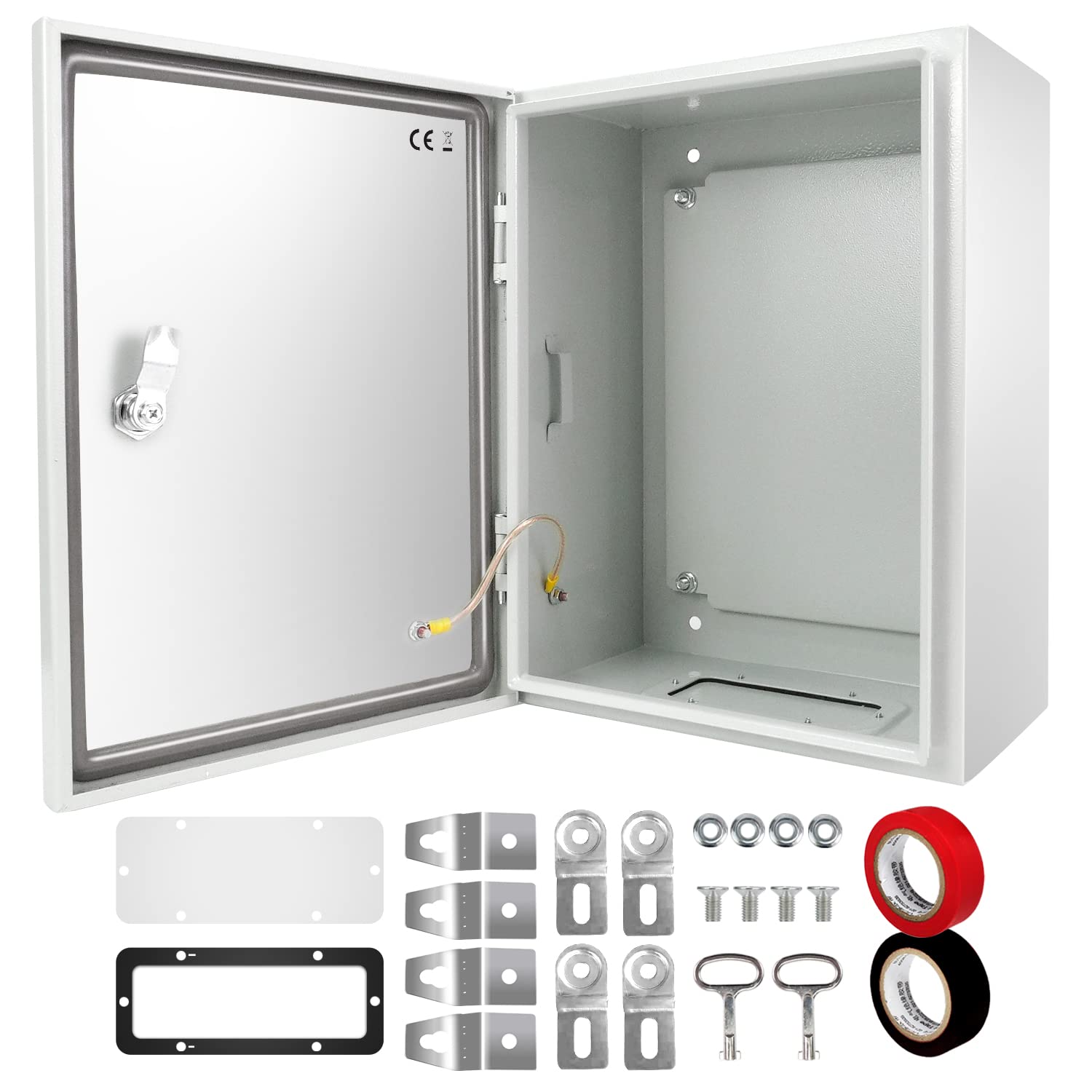
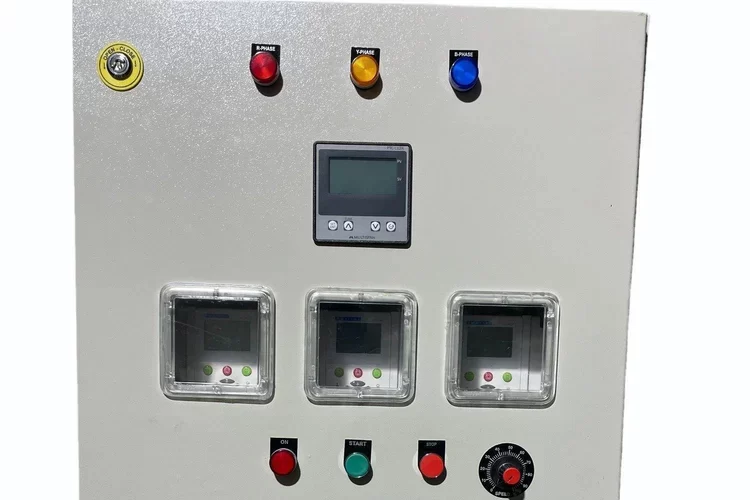
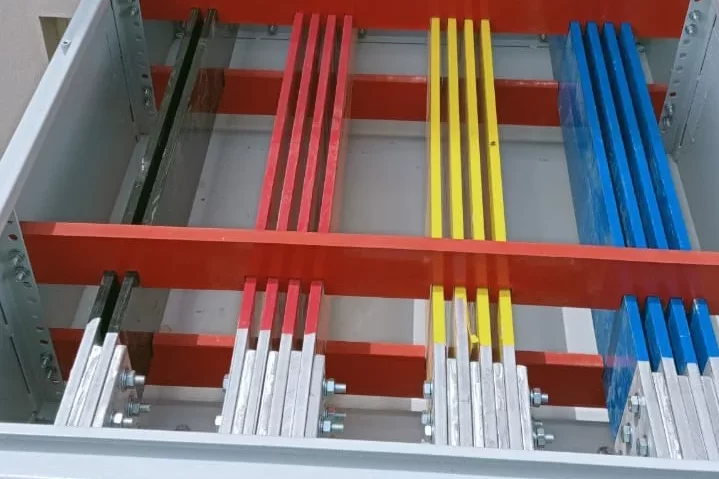
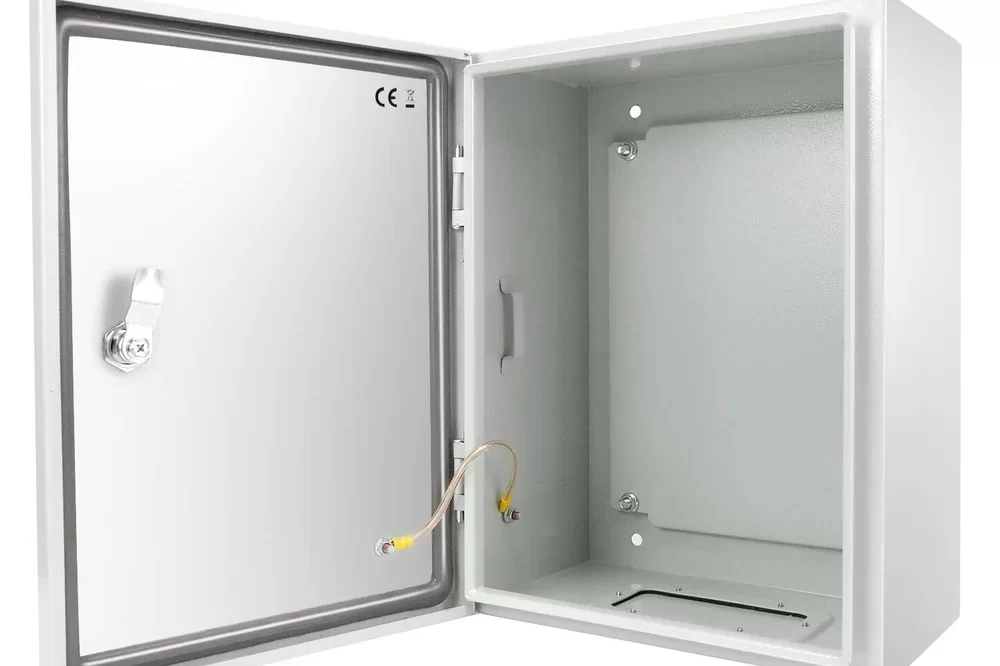
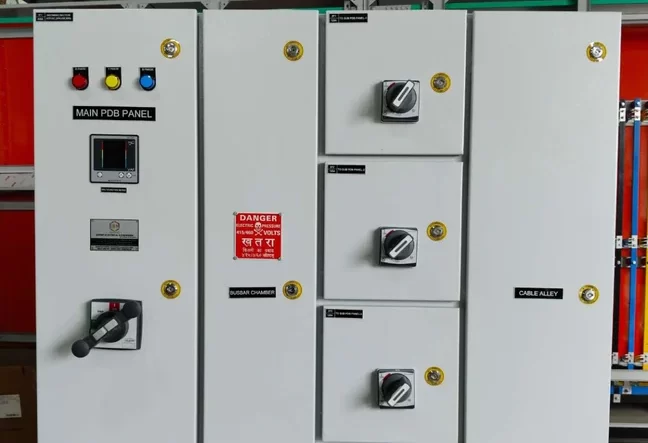
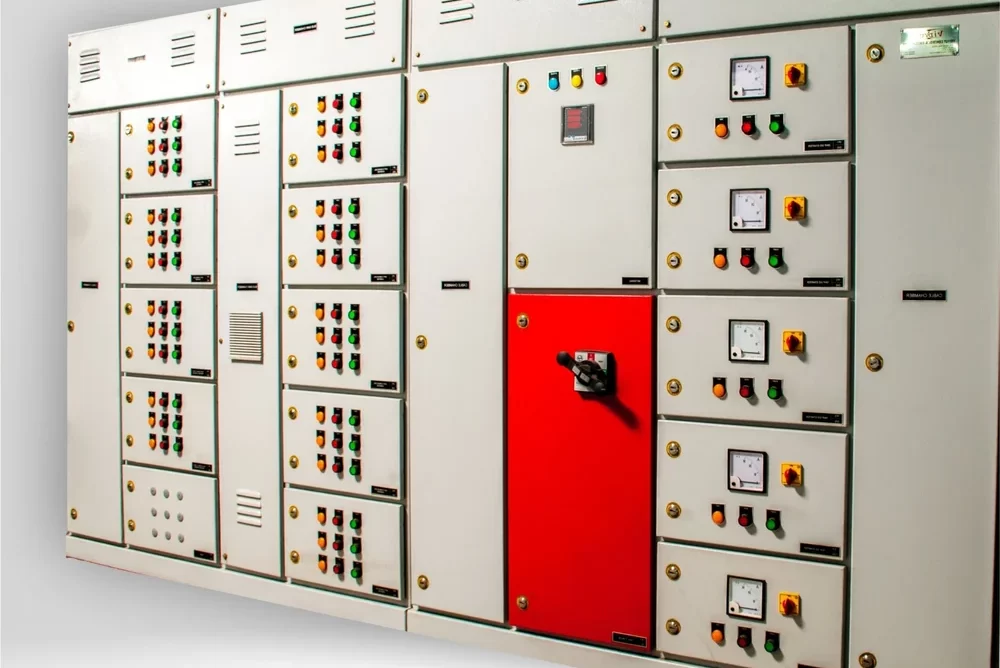
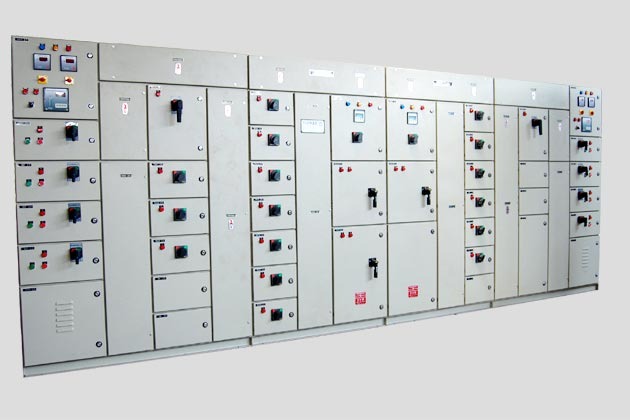
Electrical Junction Box
An Electrical Junction Box is an enclosure used in electrical systems to house and protect electrical connections and junctions. It serves as a point where multiple electrical wires or cables converge and connect to one another. Junction boxes are crucial for ensuring the safety, organization, and functionality of electrical installations.
Key Functions of an Electrical Junction Box:
- Connection Point:Provides a central location for connecting multiple electrical wires or cables. This allows for the safe and organized joining of different circuits or components.
- Protection: Protects electrical connections from environmental factors such as dust, moisture, and physical damage. The enclosure prevents accidental contact with live wires and reduces the risk of electrical shock.
- Safety: Helps prevent electrical fires by containing and managing connections, reducing the risk of short circuits or overheating. It also provides a secure and isolated space for electrical splices and terminations.
- Organization: Keeps wiring organized and accessible, making it easier to manage and troubleshoot electrical systems. The junction box allows for neat and tidy cable management.
- Code Compliance: Ensures that electrical connections are made in accordance with electrical codes and standards, which often require junction boxes for safety and reliability.
- Expansion and Modification: Allows for future expansion or modification of electrical systems by providing additional connection points. This is useful for adding new circuits or updating existing ones.
In an Electrical Junction Box, various abbreviations and symbols are used to represent components, connections, and functions. These abbreviations and symbols help in understanding electrical diagrams and ensuring proper installation and maintenance. Here’s a guide to common electrical abbreviations and symbols used in junction boxes:
J/B – Junction Box
C – Cable
P – Plug
S – Socket
L – Light (or Lamp)
T – Terminal
CB – Circuit Breaker
FUSE – Fuse
GND – Ground (or Earth)
N – Neutral
L1, L2, L3 – Live Conductors (Phases)
T1, T2, T3 – Terminals
MCB – Miniature Circuit Breaker
RCBO – Residual Current Breaker with Overcurrent Protection
RCCB – Residual Current Circuit Breaker (Earth Leakage Circuit Breaker)
ISOL – Isolator
SPD – Surge Protection Device
MT – Meter (Energy Meter)
TR – Transformer
SENSOR – Sensor
DIM – Dimmer
TIM – Timer
AMP – Ampere (Current)
V – Voltage
Junction Box Symbol:Represents the junction box itself, typically shown as a rectangle or square with lines connecting to it.
Cable Entry Symbol:Represents the entry points for cables into the junction box.
Terminal Block Symbol:Represents the connection points inside the junction box for securing wires.
Circuit Breaker Symbol:Represents a device that automatically interrupts the circuit in case of overload or short circuit.
Fuse Symbol:Represents a protective device that disconnects the circuit when an overcurrent occurs.
Isolator Symbol:Represents a switch used to disconnect a circuit for maintenance.
Surge Protection Device (SPD) Symbol:Represents a device that protects the system from voltage spikes.
Grounding Symbol:Represents the ground connection.
Neutral Symbol:Represents the neutral connection.
Live Wire Symbols:Represents live conductors, often labeled L1, L2, L3.
Meter Symbol:Represents an energy meter for measuring electrical consumption.
Dimmer Symbol:Represents a device used to adjust lighting brightness.
Sensor Symbol:Represents devices like motion sensors or daylight sensors.
Timer Symbol:Represents a timer used for automated control.
Plug and Socket Symbols:Represents power plugs and sockets connected to the junction box.
Light/Lamp Symbol:Represents lighting fixtures connected to the junction box.
An Electrical Junction Box is used to manage and protect electrical connections within a building or facility. It serves as a crucial component in electrical systems, ensuring that electrical wiring is organized, safe, and functional. Here are the primary uses and functions of an electrical junction box:
Uses of an Electrical Junction Box:
1.Connecting Electrical Wires:
Purpose: Junction boxes provide a secure and accessible point for connecting multiple electrical wires or cables together. This is essential for extending circuits or joining different sections of wiring.
Example: Connecting wires from a main power supply to individual circuits for lighting and outlets.
2.Protecting Electrical Connections:
Purpose: The junction box protects electrical connections from environmental factors such as dust, moisture, and physical damage. It also prevents accidental contact with live wires, reducing the risk of electrical shock.
Example: Using a weatherproof junction box for outdoor lighting connections to prevent moisture ingress.
3.Organizing Wiring:
Purpose: Junction boxes help organize and manage wiring by providing a central location where multiple wires can be neatly connected and routed. This organization makes it easier to maintain and troubleshoot electrical systems.
Example: Housing wiring connections in a ceiling junction box for a ceiling fan or light fixture.
4.Ensuring Safety:
Purpose: By containing and securing electrical connections, junction boxes reduce the risk of electrical faults, short circuits, and fires. They also help in maintaining compliance with electrical codes and standards.
Example: Using an explosion-proof junction box in hazardous environments to prevent sparks from igniting flammable materials.
5.Facilitating Maintenance and Repairs:
Purpose: Junction boxes provide a convenient access point for inspecting, maintaining, or repairing electrical connections. This access helps ensure that any issues can be addressed quickly and safely.
Example: Accessing a junction box in a commercial building to replace a faulty wire connection or circuit breaker.
6.Supporting System Expansion:
Purpose: Junction boxes allow for the expansion or modification of electrical systems by providing additional connection points. This is useful for adding new circuits or upgrading existing ones.
Example: Adding a new lighting circuit in a residential junction box to accommodate additional fixtures.
Functions of an Electrical Junction Box:
1.Housing Electrical Connections:
Function: Provides an enclosure for housing electrical connections, ensuring they are protected from external elements and physical damage.
Details: The box typically includes a cover or lid that can be removed for access to the connections inside.
2.Providing Wire Termination Points:
Function: Acts as a termination point for wires, allowing for the secure connection and splicing of electrical conductors.
Details: Includes terminals or connectors where wires are joined and secured.
3.Supporting Cable Management:
Function: Facilitates cable management by organizing and routing wires within the box. This helps prevent tangling and simplifies maintenance.
Details: Features cable entries or knockouts where cables can be routed into the box.
4.Offering Protection Against Electrical Faults:
Function: Protects against electrical faults such as short circuits and overloads by containing and managing connections.
Details: May include protective devices like fuses or circuit breakers, depending on the application.
5.Providing Accessibility:
Function: Offers accessibility to electrical connections for maintenance, inspection, and troubleshooting.
Details: The box can be accessed by removing the cover, allowing for easy examination and repairs.
6.Ensuring Compliance with Electrical Codes:
Function: Ensures that electrical installations meet safety standards and building codes by providing a safe and organized method for making electrical connections.
Details: Junction boxes must be installed according to local electrical codes and standards.