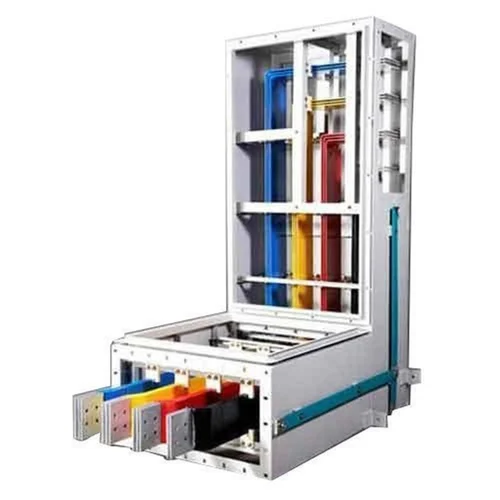
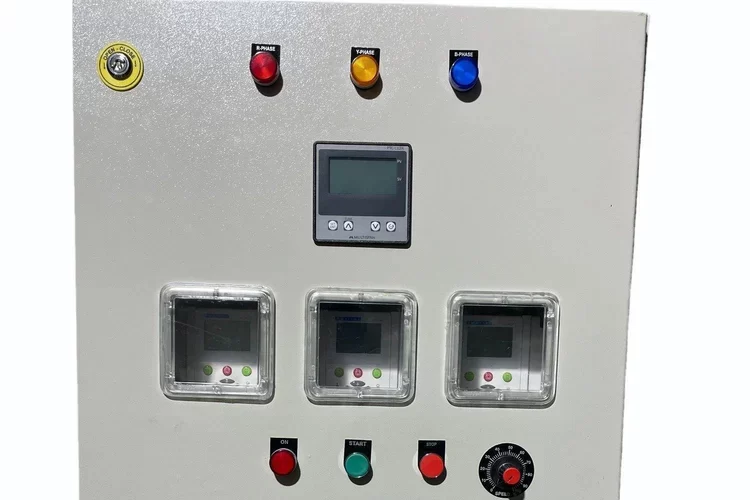
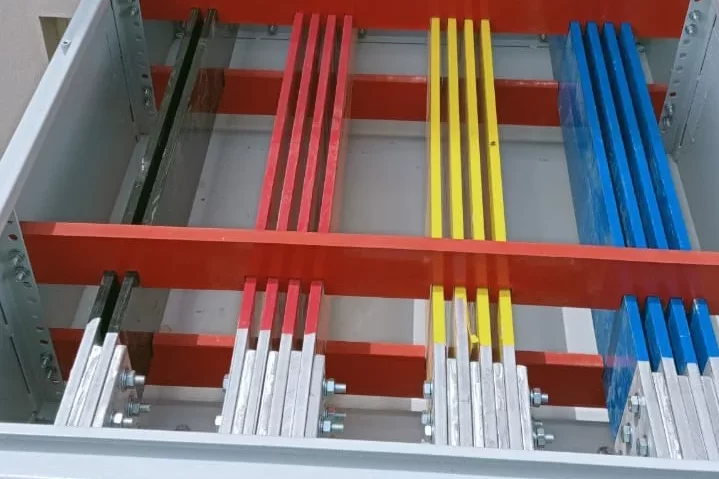
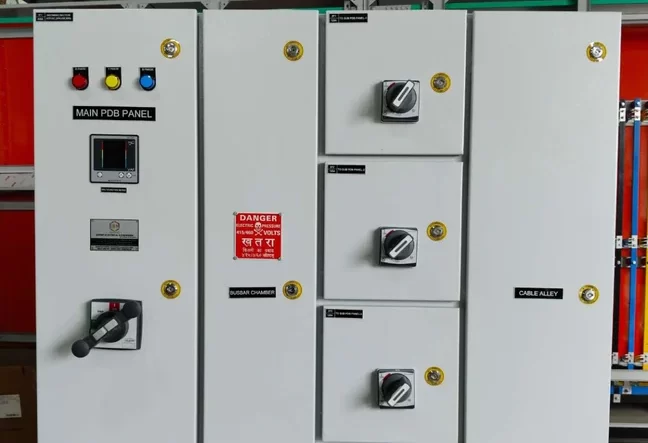
Bus Duct (upto 6300 Amp)
A Bus Duct (or busway) is an electrical distribution system used to distribute high-current electrical power within a facility. It is designed to handle large amounts of current and is often used in commercial and industrial settings to distribute electricity efficiently and safely. The rating “up to 6300 Amp” indicates that this particular bus duct system is designed to handle currents up to 6300 amperes.
Key Features of Bus Duct:
- High Current Capacity: Designed to handle high electrical currents, up to 6300 amps in this case, making it suitable for large-scale power distribution.
- Compact and Efficient Design:Consists of a metal enclosure that houses conductive busbars. This design allows for a compact and space-efficient solution compared to traditional cabling systems.
- Modular Construction:Bus ducts are often modular, allowing for easy expansion and modification. This flexibility helps in adapting to changing power distribution needs.
- Ease of Installation: Generally easier and quicker to install than traditional wiring methods, especially in large installations. Bus ducts are pre-assembled and can be mounted on supports.
- Reduced Electrical Losses: Designed to minimize electrical losses due to their low impedance and efficient conductors.
- Safety Features: Equipped with features to prevent overheating, short circuits, and electrical faults. Some systems include built-in protection devices and monitoring capabilities.
- Flexibility in Configuration:Allows for various configurations and routing options to suit different building layouts and power distribution requirements.
In bus duct systems, electrical abbreviations and symbols are used to represent various components and functions related to power distribution. Here’s a guide to some common abbreviations and symbols associated with bus ducts:
BD – Bus Duct
BB – Bus Bar
SB – Switch Board
CB – Circuit Breaker
MCCB – Molded Case Circuit Breaker
F – Fuse
PDB – Power Distribution Board
J/B – Junction Box
DP – Distribution Panel
TAP – Tap-off (or Tap-Off Box)
T – Terminal
ISOL – Isolator
SPD – Surge Protection Device
GND – Ground (or Earth)
L1, L2, L3 – Live Conductors (Phases)
N – Neutral
V – Voltage
A – Ampere (Current)
RCBO – Residual Current Breaker with Overcurrent Protection
RCCB – Residual Current Circuit Breaker
Bus Duct Symbol:Represents the bus duct system in a diagram.
Bus Bar Symbol:Represents the conductive bars inside the bus duct.
Bus Duct Tap-off Unit Symbol:Represents a tap-off unit that branches off from the main bus duct.
Circuit Breaker Symbol:Represents a circuit breaker within the bus duct system.
Fuse Symbol:Represents a fuse used for protection in the bus duct system.
Isolator Symbol:Represents an isolator switch used to disconnect the bus duct system.
Surge Protection Device (SPD) Symbol:Represents a device that protects the system from voltage spikes.
Grounding Symbol:Represents the grounding or earthing connection.
Neutral Symbol:Represents the neutral conductor.
Live Wire Symbols:Represents live conductors or phases, often labeled L1, L2, L3.
Power Distribution Board (PDB) Symbol:Represents a board used for power distribution, often associated with the bus duct system.
Bus Duct Support Symbol:Represents the supports or brackets used to mount the bus duct.
Access Door Symbol:Represents an access door or panel for maintenance.
Meter Symbol:Represents an energy meter used to monitor power usage.
Bus Duct (or busway) is a key component in electrical power distribution systems, used to efficiently and safely distribute large amounts of electrical power within a building or facility. Here’s a detailed overview of the uses and benefits of bus duct systems:
Uses of Bus Duct:
1.High Current Distribution:
Purpose: Bus ducts are designed to handle high current loads, making them ideal for distributing large amounts of electrical power. They can carry currents up to 6300 amps, depending on the system design.
Example: Distributing power to multiple high-power loads in a large industrial plant.
2.Space Efficiency:
Purpose: Compared to traditional cabling systems, bus ducts are more compact and efficient. They require less space, which is advantageous in environments where space is limited.
Example: Using bus ducts in a data center to distribute power to servers and other equipment without taking up excessive floor space.
3.Flexibility in Power Distribution:
Purpose: Bus ducts are modular and can be easily expanded or reconfigured to accommodate changes in power distribution needs. This flexibility makes them suitable for facilities that undergo frequent modifications.
Example: Adding new circuits or branches in a manufacturing facility as production demands change.
4.Simplified Installation:
Purpose: Bus ducts are pre-assembled and designed for straightforward installation. This can reduce installation time and labor compared to traditional wiring methods.
Example: Installing bus ducts in a commercial building during the initial construction phase to streamline the power distribution setup.
5.Reduced Electrical Losses:
Purpose: Bus ducts are designed to minimize electrical losses due to their low impedance and efficient conductors. This enhances overall system efficiency.
Example: Implementing bus ducts in a large power distribution network to ensure minimal energy loss and optimal performance.
6.Enhanced Safety:
Purpose: Bus ducts come with various safety features, including insulation and protection against electrical faults. They help in maintaining safe and reliable power distribution.
Example: Using bus ducts with built-in surge protection and fault isolation in a high-voltage electrical system.
7.Improved Maintenance and Access:
Purpose: The modular design of bus ducts allows for easy access to electrical connections for maintenance and troubleshooting. This helps in quickly addressing any issues that arise.
Example: Accessing a bus duct in a hospital to perform routine checks or repairs without disrupting the overall power supply.
Applications of Bus Duct:
1.Commercial Buildings:
Application: Distributes power to lighting, HVAC systems, and other electrical loads in office buildings, shopping malls, and other commercial spaces.
Example: Bus ducts used in a shopping mall to distribute power to various retail stores and common areas.
2.Industrial Facilities:
Application: Handles power distribution to heavy machinery, production lines, and other equipment in factories and manufacturing plants.
Example: Bus ducts used in a car manufacturing plant to supply power to assembly line equipment and machinery.
3.Data Centers:
Application: Provides reliable and efficient power distribution to servers, cooling systems, and other critical infrastructure in data centers.
Example: Bus ducts used in a data center to ensure stable power supply to high-density server racks.
4.Power Plants:
Application: Distributes power from generators to transformers, switchgear, and other components within power generation facilities.
Example: Bus ducts used to connect generators to the main distribution network in a power plant.
5.Hospitals:
Application: Supplies power to critical medical equipment, lighting, and HVAC systems in hospitals and healthcare facilities.
Example: Bus ducts used to provide reliable power to essential equipment in an emergency room.
6.Transportation Infrastructure:
Application: Distributes power for lighting, signaling, and other electrical systems in airports, train stations, and other transportation hubs.
Example: Bus ducts used in an airport to power lighting and baggage handling systems.
7.Large-scale Infrastructure Projects:
Application: Used in large infrastructure projects such as stadiums, convention centers, and entertainment venues to handle high power demands.
Example: Bus ducts used in a sports stadium to distribute power to lighting, scoreboards, and other systems.