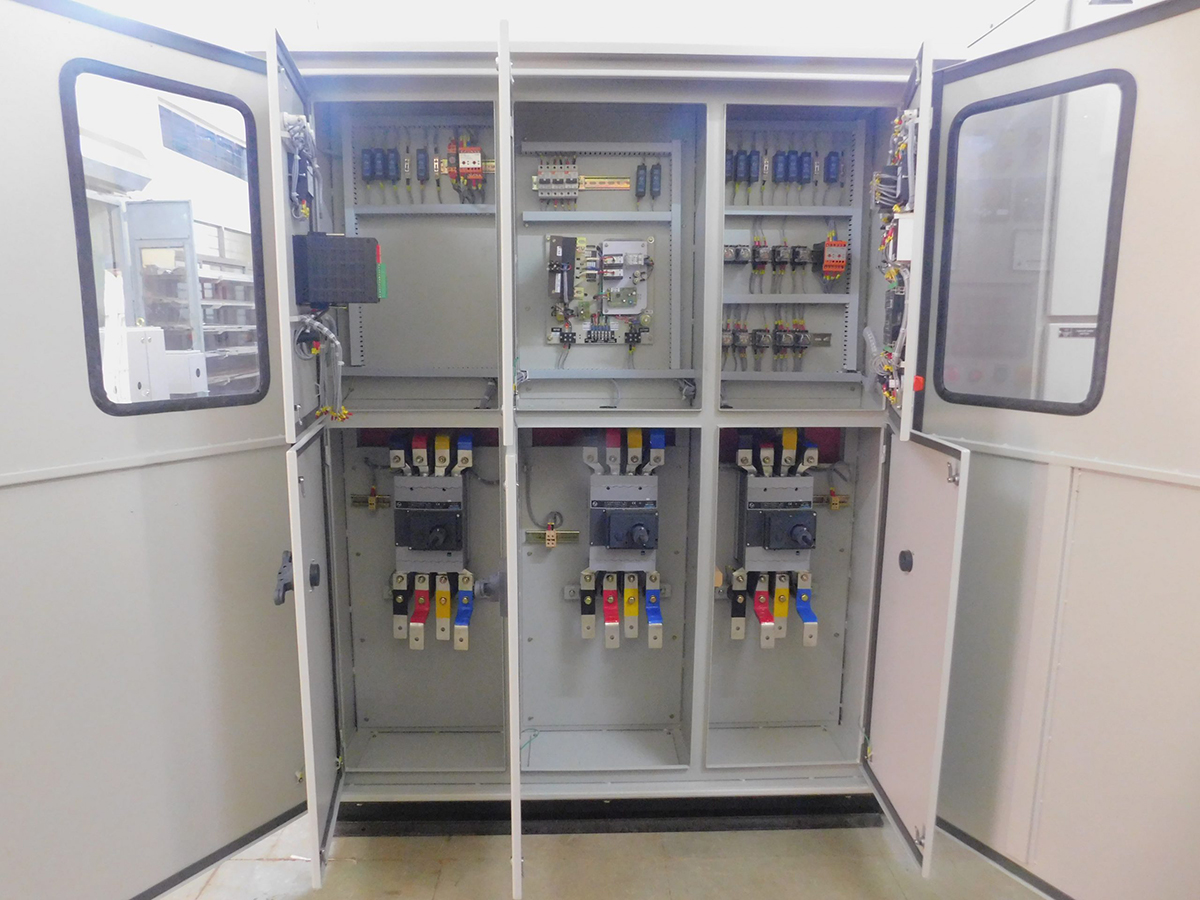
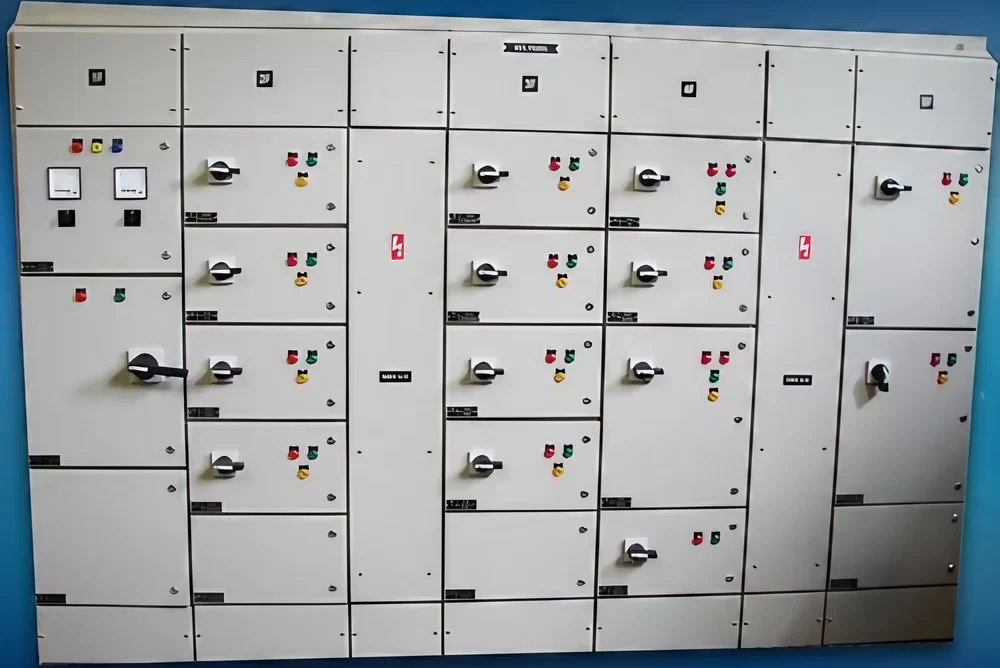
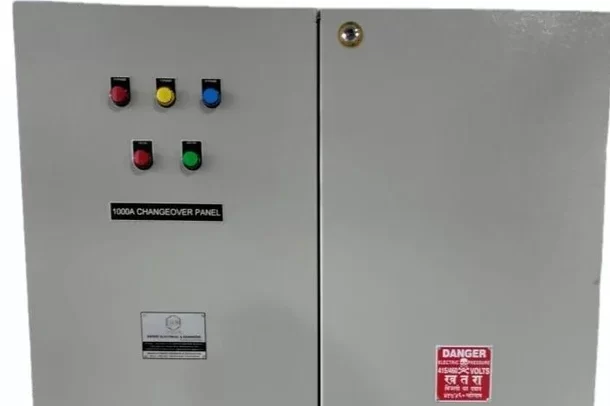
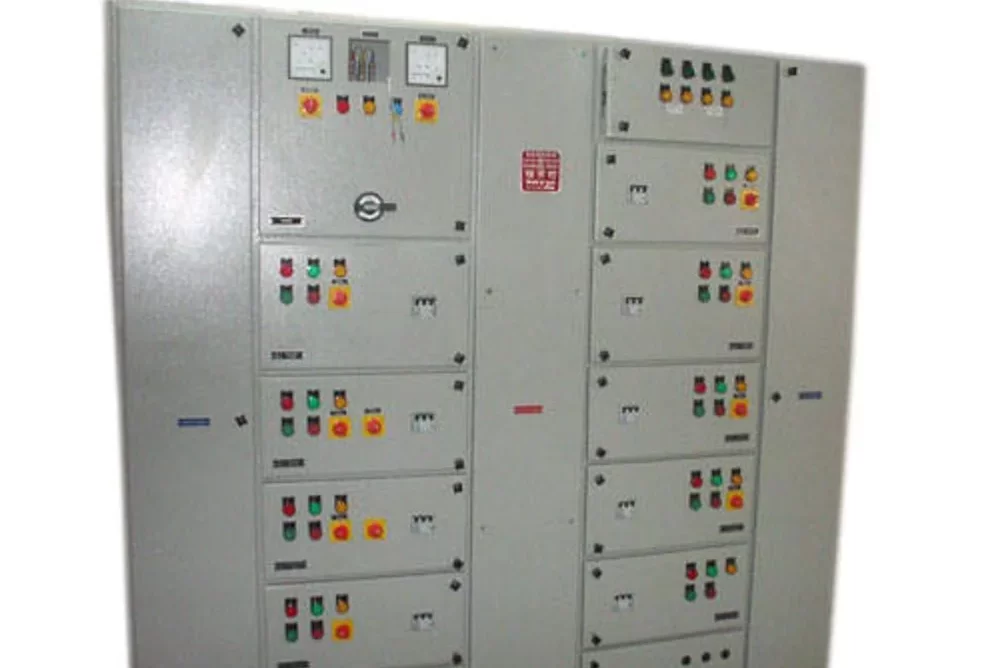
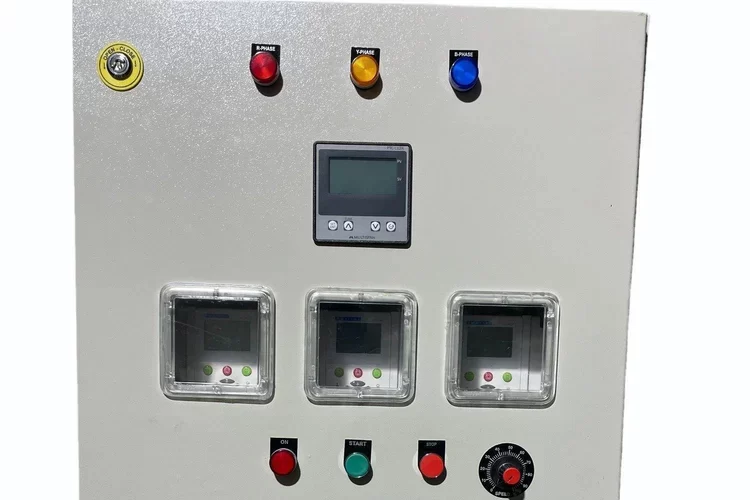
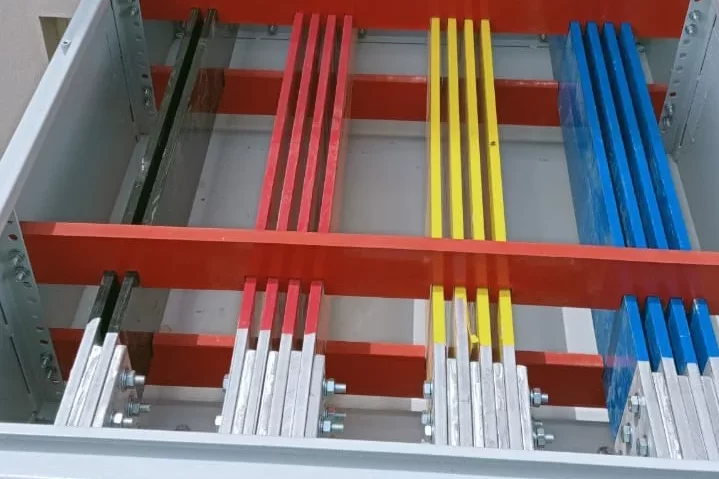
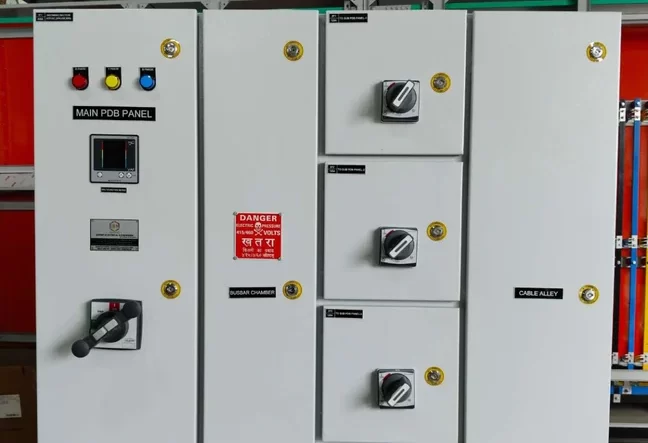
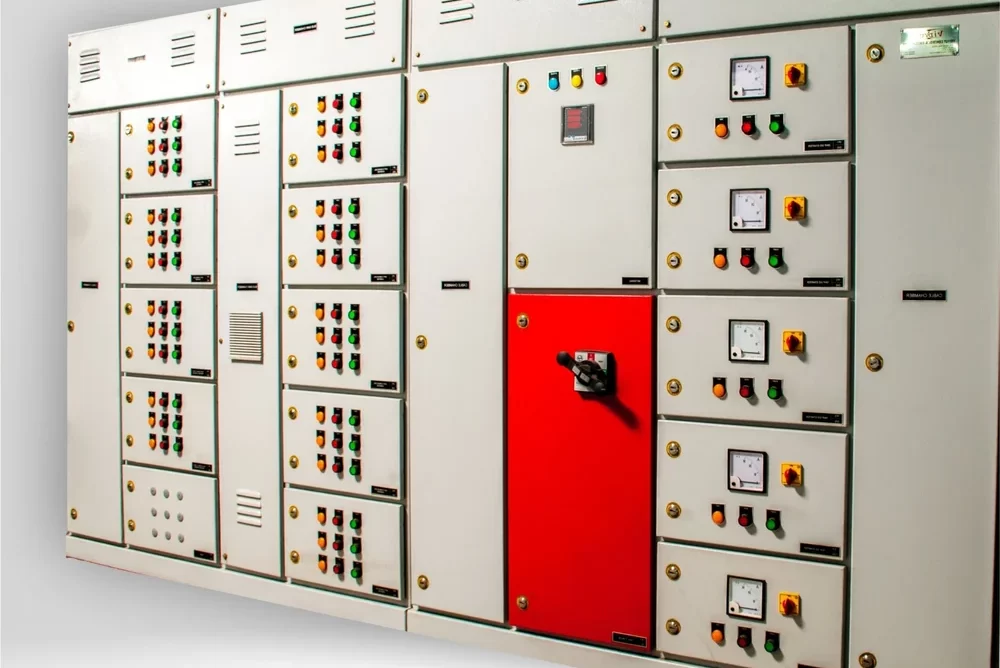
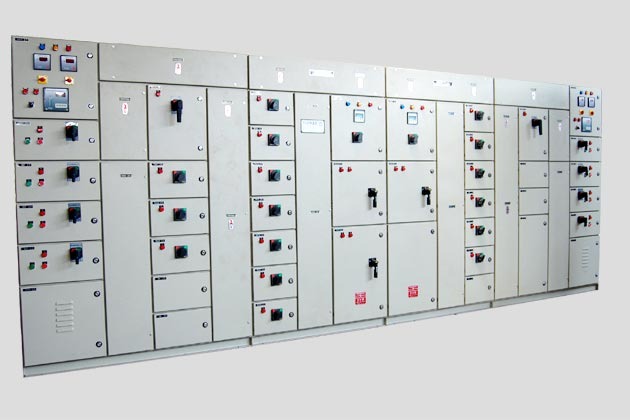
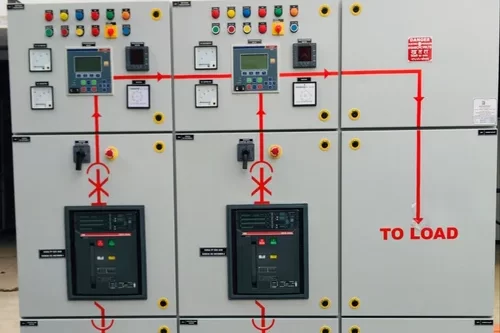
AMF Panel
An AMF Panel (Automatic Mains Failure Panel) is a type of electrical control panel that automatically switches between the main power supply and a backup generator during a power failure. This ensures a continuous power supply to critical loads without any manual intervention. AMF panels are commonly used in facilities where uninterrupted power is essential, such as hospitals, data centers, industrial plants, and commercial buildings.
Key Functions of an AMF Panel:
1.Automatic Power Source Switching:
Purpose: Automatically switches the power supply from the mains (utility) to a generator in the event of a mains power failure.
Function: Detects the loss of mains power and sends a signal to start the generator. Once the generator reaches the required parameters, the AMF panel transfers the load to the generator.
2.Generator Control:
Purpose: Manages the operation of the backup generator.
Function: Starts and stops the generator automatically based on the availability of mains power. The panel also monitors the generator’s performance and ensures it operates within safe parameters.
3.Automatic Return to Mains Power:
Purpose: Switches the power supply back to the mains when it becomes available again.
Function: Once the mains power is restored and stable, the AMF panel automatically transfers the load back to the mains and shuts down the generator after a cool-down period.
4.Protection and Safety:
Purpose: Provides protection for both the generator and the connected load.
Function: Includes features such as overcurrent protection, short-circuit protection, and under/over-voltage protection. The panel also prevents backfeeding of power into the mains, which could endanger utility workers.
5.Monitoring and Alarms:
Purpose: Provides real-time monitoring and alerting for the power supply and generator status.
Function: Displays key parameters such as voltage, frequency, and load on the panel’s interface. It also includes alarms for conditions such as generator failure, low fuel, or overheating.
6.Manual Operation (Optional):
Purpose: Allows for manual control of the power source switch if needed.
Function: Provides switches or buttons for manually starting/stopping the generator and transferring the load, useful for maintenance or troubleshooting.
In an AMF (Automatic Mains Failure) Panel, various electrical abbreviations and symbols are used to represent the components, functions, and control elements. These abbreviations and symbols are essential for understanding the panel’s operation, design, and maintenance. Here’s a comprehensive list:
AMF – Automatic Mains Failure
Function: Automatically switches the power supply from the mains to a backup generator during a power failure.
ATS – Automatic Transfer Switch
Function: Automatically transfers the load between the mains power and the generator.
GCB – Generator Circuit Breaker
Function: Connects and disconnects the generator from the load.
MCB – Miniature Circuit Breaker
Function: Provides protection against overload and short circuits for smaller circuits.
MCCB – Molded Case Circuit Breaker
Function: Provides protection against overload and short circuits for larger circuits.
RCD – Residual Current Device
Function: Detects earth faults and disconnects the circuit to prevent electric shock.
CB – Circuit Breaker
Function: General term for devices that protect electrical circuits from overload or short circuits.
CT – Current Transformer
Function: Measures the current flowing through a circuit and provides a scaled-down signal for monitoring and control.
PT – Potential Transformer
Function: Measures the voltage in a circuit and provides a scaled-down signal for monitoring and control.
HMI – Human-Machine Interface
Function: Provides a user interface for interacting with the AMF panel, including configuration and monitoring.
PLC – Programmable Logic Controller
Function: Automates the control processes within the AMF panel.
UPS – Uninterruptible Power Supply
Function: Provides backup power to critical loads during the transition from mains to generator power.
V – Voltage
Function: Represents the electrical potential difference in a circuit.
A – Ampere
Function: Represents the electrical current flowing in a circuit.
Hz – Hertz
Function: Represents the frequency of the alternating current (AC).
NO – Normally Open
Function: Refers to a contact that is open when the relay or switch is not energized.
NC – Normally Closed
Function: Refers to a contact that is closed when the relay or switch is not energized.
OL – Overload
Function: Indicates an overload condition in the circuit.
GEN – Generator
Function: Refers to the backup generator in the system.
MAINS – Mains Power Supply
Function: Refers to the main utility power source.
EF – Earth Fault
Function: Indicates a fault condition where current is leaking to the ground.
1.Automatic Transfer Switch (ATS) Symbol:
Symbol: Typically represented as a switch icon with an “ATS” label or a switch between two sources.
Function: Represents the device that switches the load between mains power and the generator.
2.Circuit Breaker (CB) Symbol:
Symbol: A rectangle or square with a line through it, labeled “CB.”
Function: Represents a circuit breaker used for protection.
3.Generator Circuit Breaker (GCB) Symbol:
Symbol: A rectangle or square with “GCB” inside or a breaker symbol with a generator icon.
Function: Represents the circuit breaker that connects or disconnects the generator.
4.Miniature Circuit Breaker (MCB) Symbol:
Symbol: A small rectangle or square with “MCB” inside.
Function: Represents a miniature circuit breaker for smaller loads.
5.Residual Current Device (RCD) Symbol:
Symbol: A rectangle with an “RCD” label or a standard RCD symbol.
Function: Represents a device that protects against earth faults.
6.Current Transformer (CT) Symbol:
Symbol: A circle with a line passing through it or a rectangle labeled “CT.”
Function: Represents a device that measures current.
7.Potential Transformer (PT) Symbol:
Symbol: A rectangle or circle with “PT.”
Function: Represents a device that measures voltage.
8.Voltage Symbol (V):
Symbol: A “V” inside a circle or square.
Function: Represents voltage measurement points.
9.Ampere Symbol (A):
Symbol: An “A” inside a circle or square.
Function: Represents current measurement points.
10.Relay Symbol:
Symbol: A rectangle with a coil inside or an icon representing a switch with “NO” and “NC” contacts.
Function: Represents a relay used for control and automation.
11.Contactor Symbol:
Symbol: A rectangle with three lines representing contacts.
Function: Represents a contactor used to switch the power on or off to a load.
12.Transformer Symbol:
Symbol: Two parallel lines with a winding symbol in between or a rectangle with a transformer label.
Function: Represents a transformer used for voltage conversion.
13.Indicator Light Symbol:
Symbol: A circle with a light bulb icon or an LED symbol.
Function: Represents an indicator light showing the status of the system.
14.Battery Symbol:
Symbol: A series of short and long lines or a battery icon.
Function: Represents a battery used in the generator starting system or UPS.
15.Earth (Ground) Symbol:
Symbol: A set of three horizontal lines decreasing in length or a standard ground symbol.
Function: Represents the connection to the earth or ground.
16.Overload Relay Symbol:
Symbol: A rectangle with a heater coil symbol or “OL.”
Function: Represents a relay that protects the circuit from overloads.
17.Human-Machine Interface (HMI) Symbol:
Symbol: A screen or panel icon with the letters “HMI.”
Function: Represents the user interface for controlling and monitoring the AMF panel.
18.Programmable Logic Controller (PLC) Symbol:
Symbol: A rectangle with the letters “PLC” or an icon representing a controller.
Function: Represents the device that controls the logic of the AMF panel.
An AMF (Automatic Mains Failure) Panel is widely used in various settings to ensure a reliable and uninterrupted power supply. Its primary function is to automatically switch from the main power supply to a backup generator in the event of a mains power failure, and then back to the mains when power is restored. Here are the key uses of an AMF panel:
1. Uninterrupted Power Supply:
Purpose: Ensures continuous power to critical systems and operations during a mains power failure.
Use: Automatically starts the backup generator and transfers the load to it, preventing downtime and loss of productivity.
2. Automatic Switching:
Purpose: Automates the transfer of power between the mains and a generator.
Use: Eliminates the need for manual intervention, ensuring a seamless transition between power sources.
3. Critical Infrastructure Support:
Purpose: Provides backup power to essential services and systems.
Use: Ensures that critical infrastructure, such as hospitals, data centers, and emergency services, remain operational during power outages.
4. Safety and Protection:
Purpose: Protects electrical equipment from damage due to sudden power loss or surges when the power returns.
Use: Includes protective features like overcurrent protection, under/over-voltage protection, and isolation of the faulty power source.
5. Remote Monitoring and Control:
Purpose: Enables monitoring and control of power sources remotely.
Use: Provides real-time status updates and alerts, allowing for quick response to power issues, which is crucial for facilities with limited on-site staff.
6. Cost-Efficient Operation:
Purpose: Reduces operational costs by optimizing generator use.
Use: Only activates the generator when needed, saving fuel and reducing wear and tear on the generator.
7. Load Management:
Purpose: Balances and manages the load between the mains and the generator.
Use: Prevents overloading of the generator and ensures that critical loads are prioritized during a power failure.
8. Maintenance Scheduling:
Purpose: Allows for the safe maintenance of the electrical system without disrupting the power supply.
Use: Operators can manually switch to the generator during maintenance of the mains supply, ensuring continuous power.
9. Redundancy for Mission-Critical Applications:
Purpose: Provides redundancy for systems that require high availability and reliability.
Use: Ensures that backup power is always available, reducing the risk of power outages in mission-critical environments.
10. Compliance with Regulatory Requirements:
Purpose: Helps facilities meet regulatory standards for emergency power systems.
Use: Many industries are required by law to have a reliable backup power system, and an AMF panel is integral to compliance.