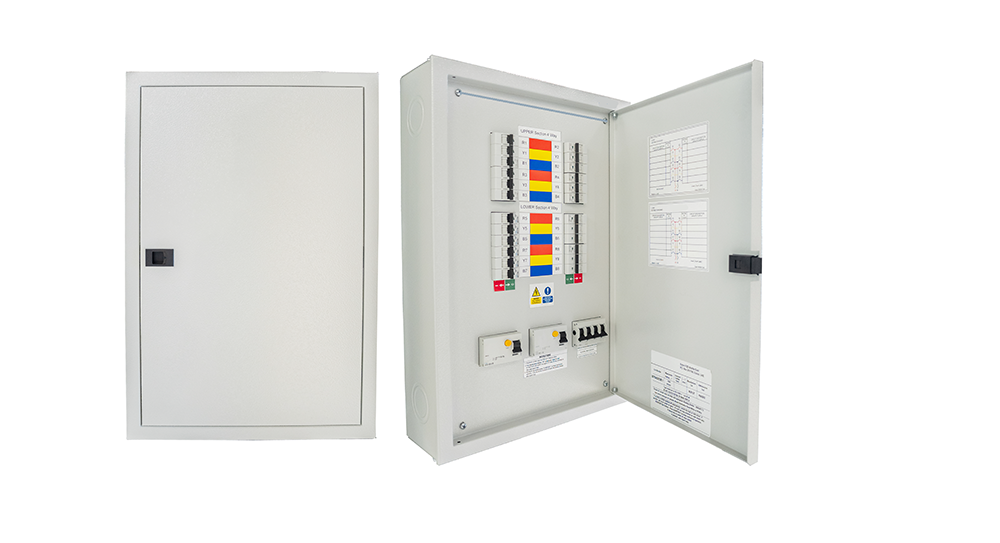
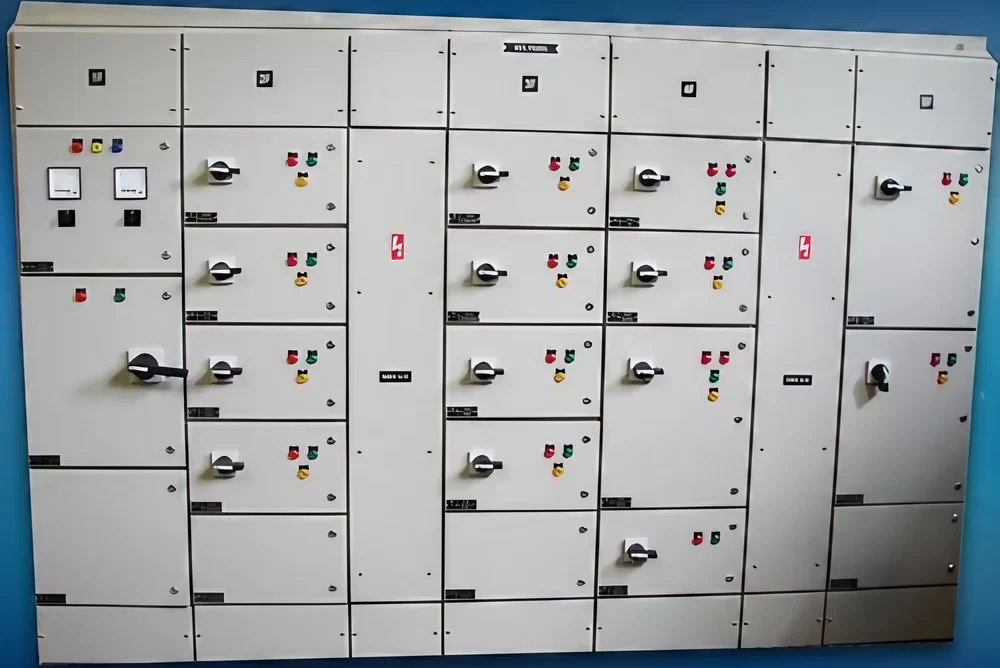
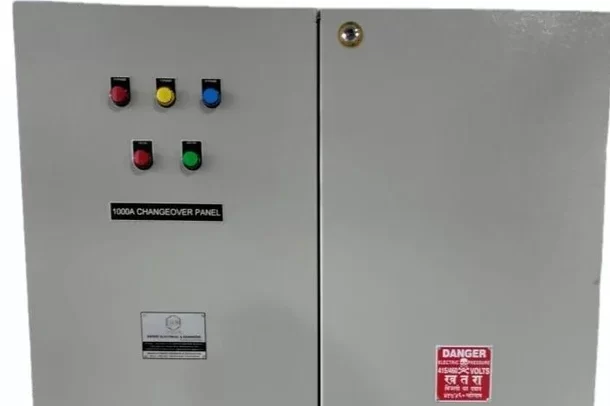
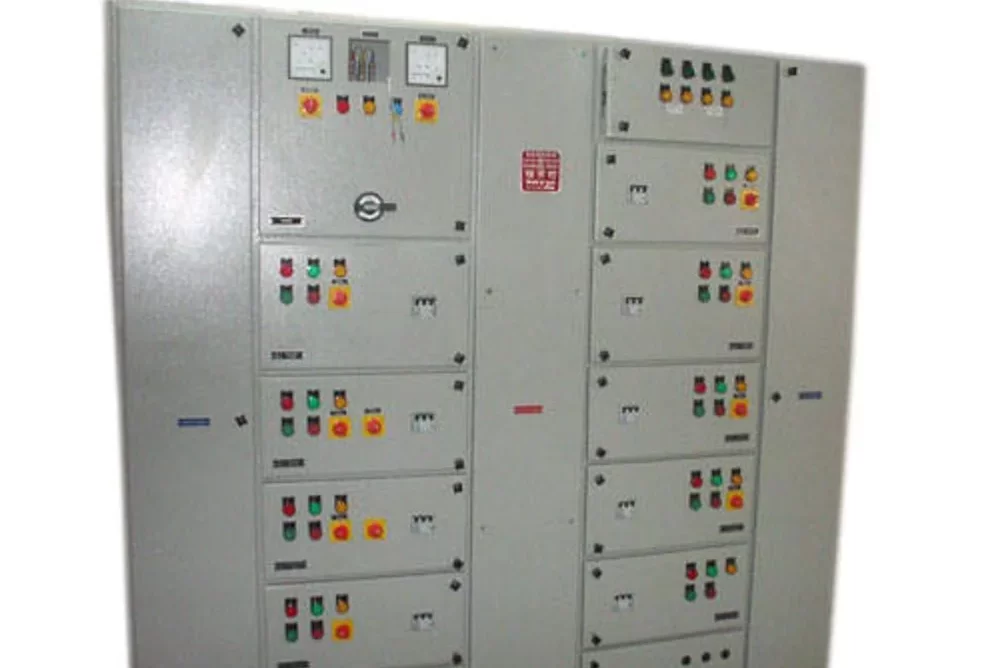
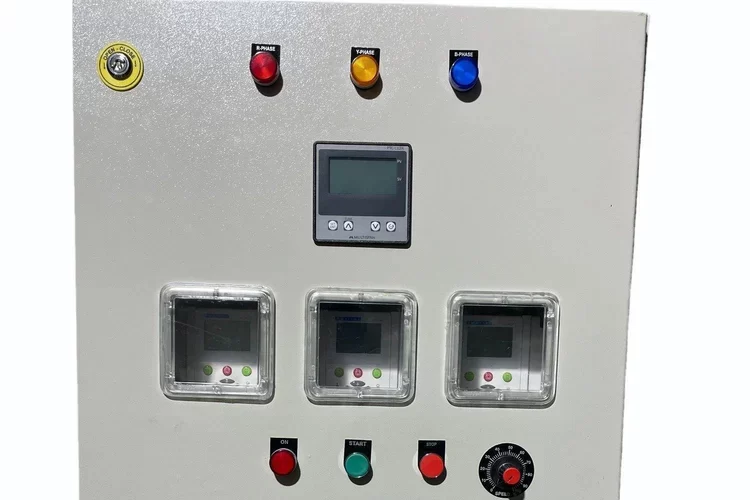
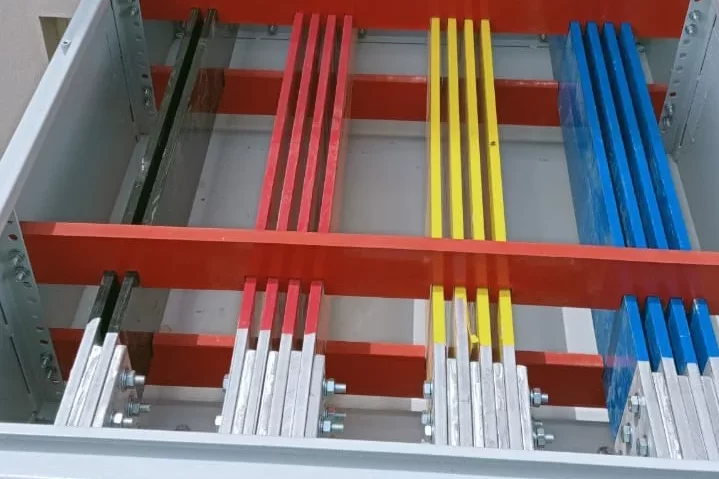
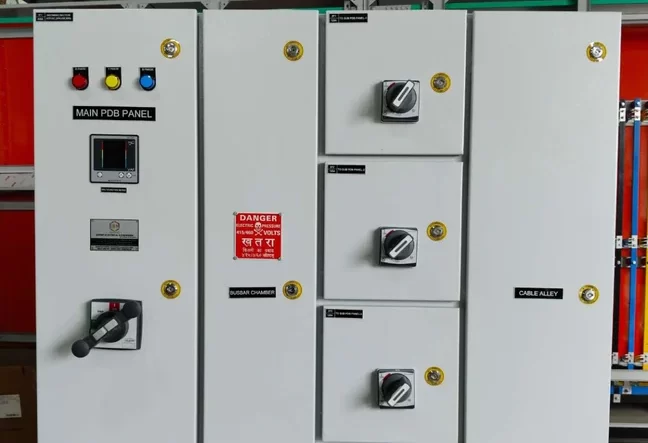
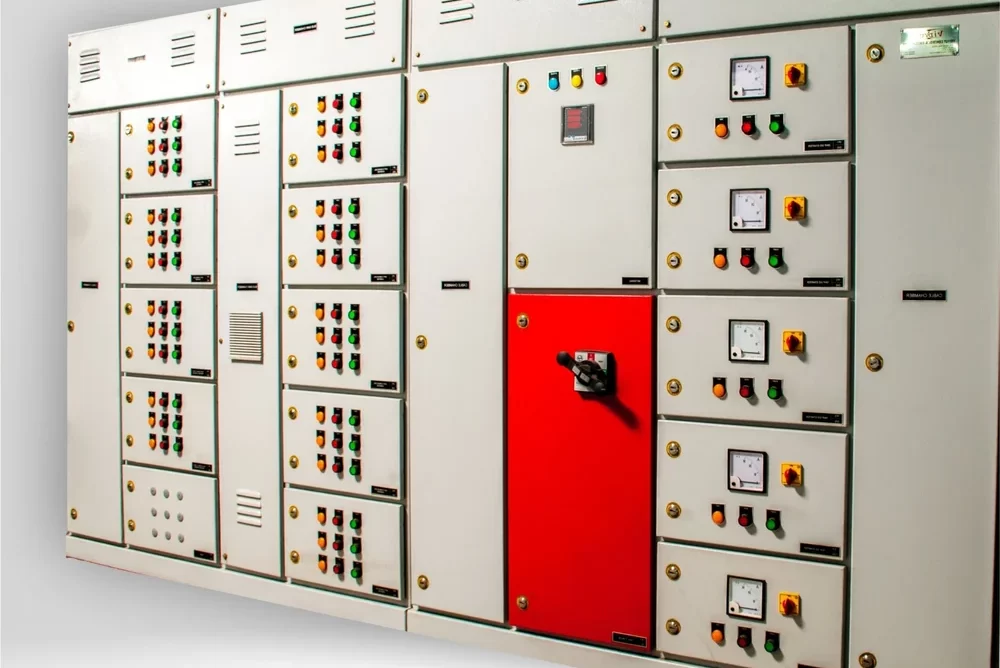
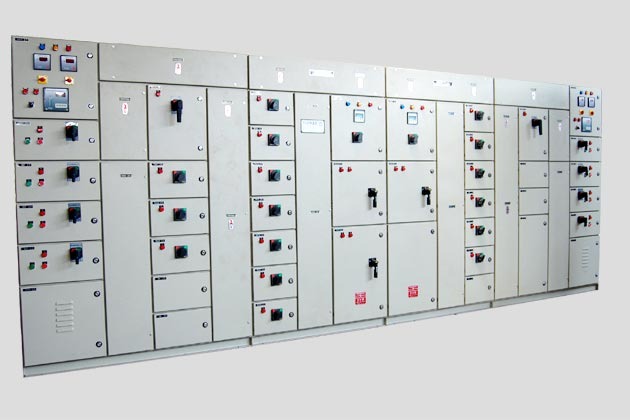
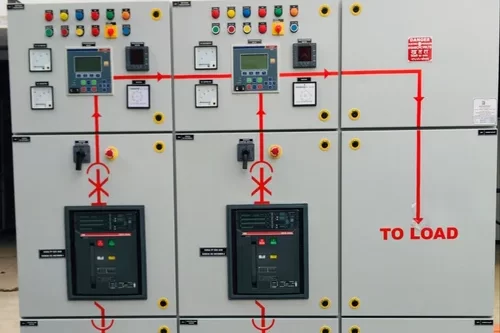
Power Distribution Board
A Power Distribution Board (PDB), also known as a Distribution Board (DB) or Panel Board, is a critical component in electrical distribution systems. It serves as a central point where electrical power is distributed to various circuits and loads within a building, facility, or infrastructure.
Functions of a Power Distribution Board:
- Power Distribution: The PDB distributes electrical power from a main source to various circuits and loads throughout the facility. It ensures that power is allocated efficiently and safely to different areas or equipment.
- Protection: It incorporates protective devices such as circuit breakers, fuses, and overload relays to safeguard electrical circuits and equipment from overcurrents, short circuits, and other faults. These devices help in preventing damage and ensuring the safety of the electrical system.
- Isolation:The PDB provides isolation capabilities, allowing certain circuits or loads to be disconnected for maintenance or repair without affecting the entire electrical system. This is typically achieved using isolators or switches.
- Monitoring: It may include metering and monitoring equipment to measure and display electrical parameters such as voltage, current, and power consumption. This helps in managing energy usage and identifying potential issues.
- Control: The PDB allows for the control of various electrical circuits and loads, enabling operators to turn circuits on or off, adjust settings, or respond to alarms and indicators.
- Safety: Ensures that the electrical system operates safely by including features such as grounding, protection against electrical faults, and proper enclosures.
- Customization: Can be customized to meet specific requirements of different applications, including the number of circuits, type of protection, and control options.
- Flexibility: Provides flexibility in managing electrical loads and circuits, allowing for future expansions or modifications as needed.
In a Power Distribution Board (PDB), various electrical abbreviations and symbols are used to represent components, functions, and measurements. Understanding these abbreviations and symbols is crucial for reading and interpreting electrical diagrams, ensuring correct installation, and performing maintenance. Here’s a comprehensive list of common abbreviations and symbols found in PDBs:
CB – Circuit Breaker
MCB – Miniature Circuit Breaker
MCCB – Molded Case Circuit Breaker
RCCB – Residual Current Circuit Breaker (Earth Leakage Circuit Breaker)
RCBO – Residual Current Circuit Breaker with Overcurrent Protection
ISOL – Isolator
CT – Current Transformer
PT – Potential Transformer (Voltage Transformer)
BU – Busbar
FUSE – Fuse
LT – Low Tension
HT – High Tension
E/M – Earth/Neutral
SPD – Surge Protection Device
M – Meter (Energy Meter)
NO – Normally Open (Contact)
NC – Normally Closed (Contact)
OLR – Overload Relay
AMP – Ampere (Current)
V – Voltage
W – Watt (Power)
kW – Kilowatt
kVAR – Kilovolt-Ampere Reactive (Reactive Power)
THD – Total Harmonic Distortion
CT/PT – Current Transformer / Potential Transformer
Circuit Breaker Symbol:Represents a device that automatically interrupts the circuit in case of overload or short circuit.
Fuse Symbol:Represents a protective device that disconnects the circuit when an overcurrent occurs.
Isolator Symbol:Represents a switch used to disconnect a circuit for maintenance.
Current Transformer (CT) Symbol:Represents a device that measures current and provides inputs to monitoring equipment.
Potential Transformer (PT) Symbol:Represents a device that measures voltage and provides it to metering equipment.
Busbar Symbol:Represents a conductor that distributes electricity within the PDB.
Meter Symbol:Represents an energy meter used to measure electrical consumption.
Surge Protection Device (SPD) Symbol:Represents a device that protects the system from voltage spikes.
Overload Relay Symbol:Represents a device that protects motors from overload conditions.
Earth/Earth Ground Symbol:Represents the grounding connection for safety.
Neutral Link Symbol:Represents the neutral connection point in the PDB.
Terminal Block Symbol:Represents connection points for wiring within the board.
Control Switch Symbol:Represents manual switches or controls used for operating equipment.
Indicator Light Symbol:Represents lights used to show the status of the system.
Ventilation Fan Symbol:Represents a fan used to cool the interior of the PDB.
HMI (Human Machine Interface) Symbol:Represents the interface used for monitoring and controlling the PDB.
Alarm Symbol:Represents devices used for signaling alarms or alerts.
A Power Distribution Board (PDB) is a central component in electrical distribution systems used to manage, distribute, and control electrical power within various environments. Here’s an overview of the typical uses and functions of a PDB:
1.Commercial Buildings:
Office Buildings: Distributes power to different floors or departments, including lighting, HVAC systems, and office equipment.
Shopping Malls: Manages power distribution to various stores, common areas, and facilities like escalators and security systems.
Hotels: Distributes power to guest rooms, restaurants, laundry facilities, and other hotel amenities.
2.Industrial Facilities:
Factories: Provides power to machinery, production lines, and equipment, ensuring operational efficiency and safety.
Manufacturing Plants: Manages power distribution for complex processes and heavy-duty equipment used in manufacturing.
3.Residential Buildings:
Homes: Distributes power to lighting, appliances, heating and cooling systems, and other household circuits.
Apartments: Manages power for individual units, common areas, and shared facilities in multi-family buildings.
4.Infrastructure Projects:
Airports: Distributes power to terminal facilities, baggage handling systems, lighting, and other critical infrastructure.
Hospitals: Ensures reliable power supply to medical equipment, lighting, HVAC systems, and emergency services.
5.Public Utilities:
Power Stations: Distributes electricity from power generation sources to various parts of the grid or directly to consumers.
Water Treatment Plants: Manages power distribution for treatment processes, pumps, and control systems.
6.Transportation Systems:
Railways: Distributes power to signaling systems, track switches, and other railway infrastructure.
Subways and Metro Systems: Manages power distribution for trains, lighting, ventilation, and signaling.
7.Renewable Energy Systems:
Solar Farms: Distributes power generated from solar panels to the grid or local consumption points.
Wind Farms: Manages the distribution of electricity generated from wind turbines to the grid or local users.
8.Data Centers:
Server Rooms: Ensures reliable power supply to servers, cooling systems, and other IT infrastructure.
9.Educational Institutions:
Schools and Universities: Distributes power to classrooms, laboratories, administrative offices, and recreational facilities.
10.Retail and Hospitality:
Restaurants and Cafes: Manages power for kitchen equipment, lighting, HVAC systems, and customer areas.
In summary, a Power Distribution Board is essential for managing and controlling the distribution of electrical power in various environments. It ensures that power is distributed safely and efficiently to different circuits and loads, providing protection, control, and monitoring to maintain reliable operation.